One Vehicle, One FASTag
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
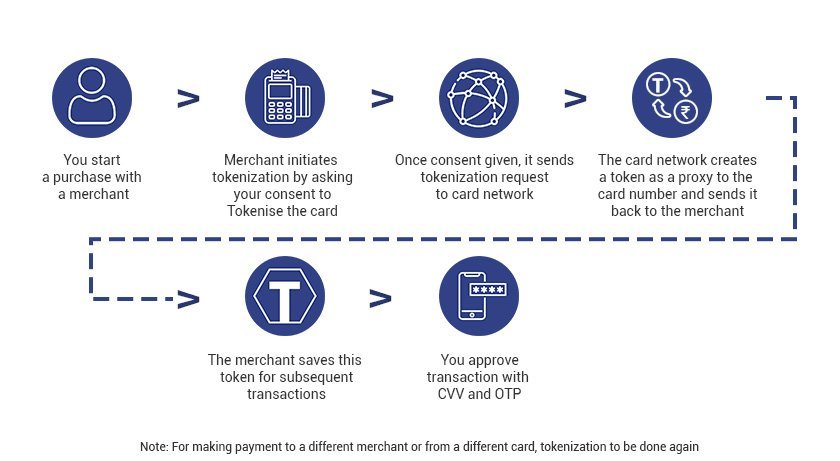
- Context (PIB): The National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) has introduced the ‘One Vehicle, One FASTag‘ initiative.
- It aims to enhance the efficiency of the Electronic Toll Collection system and provide seamless movement at the Toll Plazas.
- The initiative would discourage using a single FASTag for multiple vehicles or associating multiple FASTags with a single vehicle.
- FASTags with a valid balance but incomplete KYC will be deactivated/blocked after January 31, 2024.
FASTags
- FASTag is an electronic toll collection system, launched in 2016.
- It is operated by the National Highways Authority of India (NHAI).
- The device employs Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology for payments directly from the prepaid or savings account linked to it.
- It is affixed on the windscreen, so the vehicle can drive through plazas without stopping.
- It is valid for five years & can be recharged as & when required.
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID)
- RFID is an acronym for “radio-frequency identification” & refers to a technology whereby digital data encoded in RFID tags or smart labels are captured by a reader via radio waves.
- RFID belongs to a group of technologies referred to as Automatic Identification & Data Capture.
- AIDC methods automatically identify objects, collect data about them, & enter those data directly into computer systems with little or no human intervention.
- RFID tags contain an integrated circuit & an antenna, which transmit data to the RFID reader (interrogator).
- The reader then converts the radio waves to a more usable form of data.
- Information collected from the tags is stored in a database & analysed.
- RFID is like barcoding in that data from a tag is captured by a device that stores the data in a database.
- RFID, however, has several advantages over systems that use barcode asset tracking software.
- The most notable is that RFID tag data can be read outside the line-of-sight, whereas barcodes must be aligned with an optical scanner.






![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)