Embedded SIM for Machine-to-Machine Communications
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
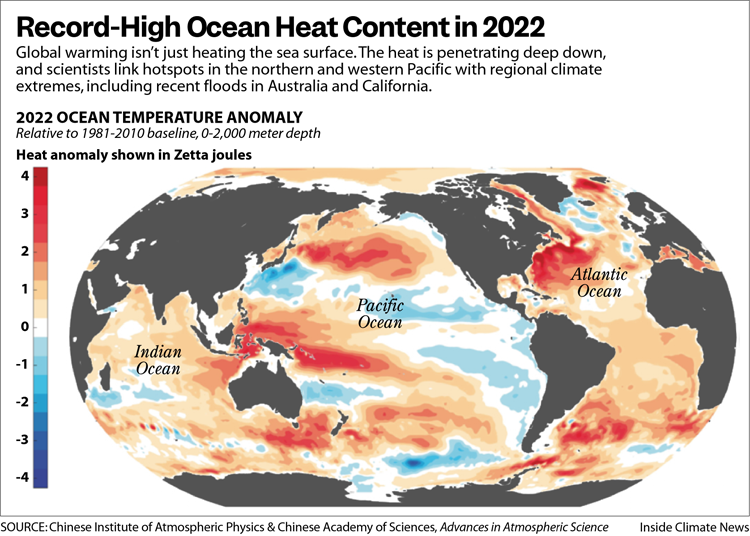
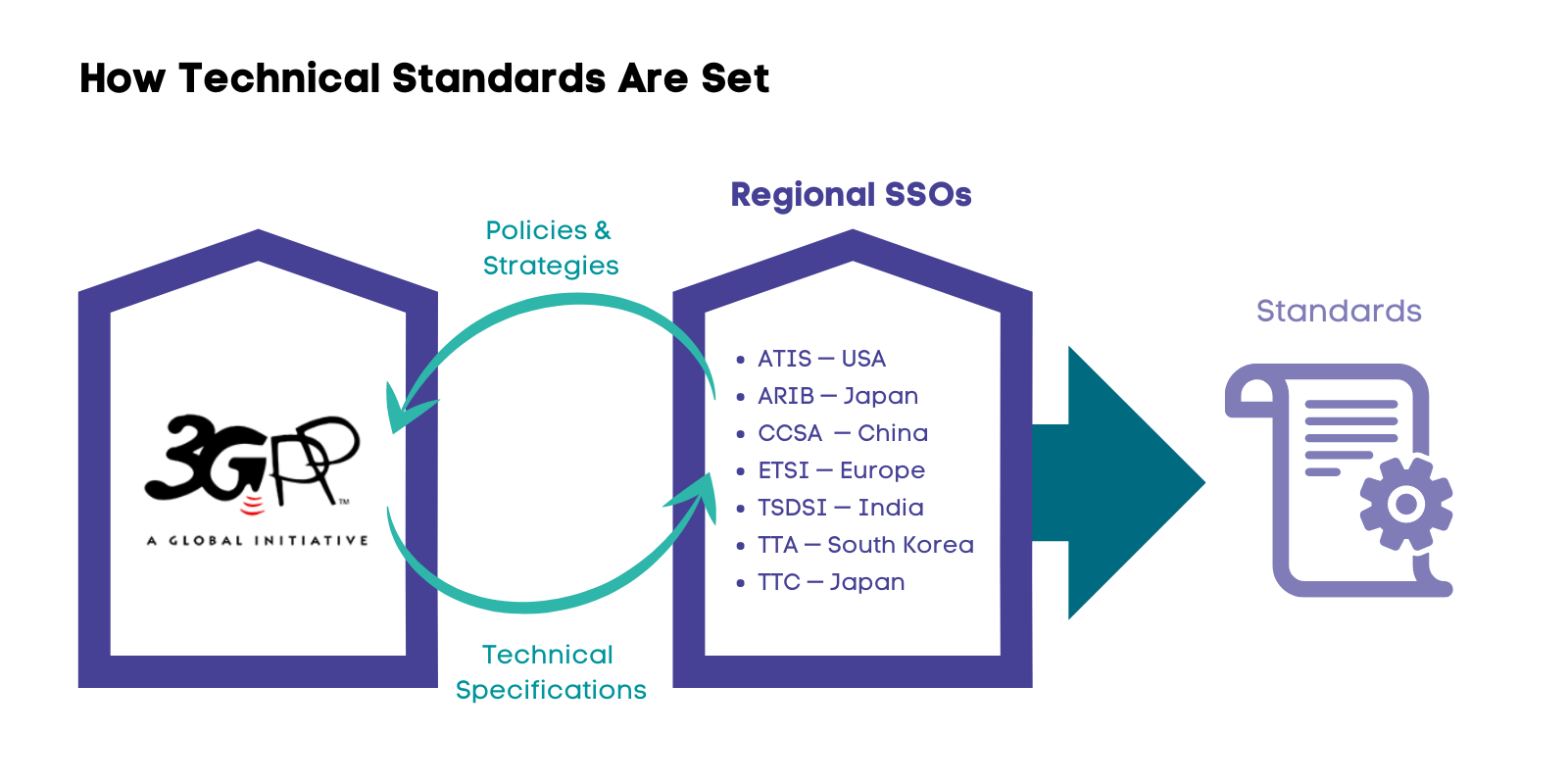
- Context (PIB): The Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) has recently released recommendations regarding the usage of Embedded SIM (eSIM) for Machine-to-Machine (M2M) communications.
- The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) sought TRAI’s recommendations on the usage of eSIM for M2M communications in 2021.
What is Embedded SIM (eSIM)?
- An eSIM is specifically designed for IoT sensors, meters, trackers, and devices that often operate with minimal human interaction on-site.
- These SIMs are embedded (integrated/soldered) during manufacturing to meet standard physical and environmental requirements.
- They can be deployed in both domestic and international markets.
Advantages of eSIM (Embedded SIM) over Traditional SIM cards

What is Machine-to-Machine (M2M) communication?
- Machine-to-machine (M2M) communication refers to the exchange of data between devices without human intervention.
- In this, devices interact directly with each other, seamlessly sharing information and performing actions based on the received data.
- M2M communication involves entities such as sensors, machines, vehicles, or measuring equipment that operate independently.
Key Features
- Low Mobility: M2M devices are stationary, move infrequently, or operate within specific regions.
- Time Controlled: Data transmission occurs at predefined intervals.
- Time Tolerant: Data transfer can be delayed.
- Packet Switched: Network operators provide packet-switched services.
- Online Small Data Transmissions: MTC devices frequently send or receive small amounts of data.
- Monitoring: Detecting events (e.g., theft or vandalism).
- Low Power Consumption: Efficiently servicing M2M applications.
- Location-Specific Triggers: Triggering M2M devices in specific areas.
Applications
- Security: Surveillance systems, alarm systems, access control, and car/driver security.
- Tracking & Tracing: Fleet management, order management, asset tracking, navigation, and traffic optimization.
- Payment: Point-of-sale systems, vending machines, and gaming machines.
- Health: Monitoring vital signs, supporting the aged or handicapped, telemedicine points, and remote diagnostics.
- Remote Maintenance/Control: This includes controlling sensors, lighting, pumps, valves, elevators, vending machines, and vehicle diagnostics.
- Metering: Monitoring power, gas, water, heating, and industrial metering.
- Manufacturing: Production chain monitoring and automation.
- Facility Management: Automation in homes, buildings, and campuses.
How does M2M communication differ from IoT?
| M2M | Internet of Things (IoT) |
| M2M is about direct communication between machines. | IoT is about sensors automation and internet platform. |
| It supports point-to-point communication. | It supports cloud communication |
| Devices do not necessarily rely on internet connection | Devices rely on an internet connection. |
| It is mostly hardware-based technology | Both hardware and software-based technology. |
| Machines normally communicate with a single machine at a time | Many users can access at one time over the internet. |
| A device can be connected through mobile or another network. | Data delivery depends on the Internet Protocol (IP) network. |





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)