Design Linked Incentive (DLI) Scheme
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
- Context (TH): The semiconductor Design-Linked Incentive (DLI) scheme has approved just seven start-ups, far below its five-year target of 100. Policymakers have an opportunity to reassess and enhance the scheme.
Design Linked Incentive (DLI) Scheme
- It aims to offer financial incentives as well as design infrastructure support across various stages of development and deployment of semiconductor design(s).
- Target Segments: Semiconductor design for Integrated Circuits (ICs), Chipsets, System on Chips (SoCs), Systems & IP Cores and semiconductor-linked design.
- Nodal agency: C-DAC (Centre for Development of Advanced Computing), operating under MeitY.
- Aim: To nurture at least 20 domestic companies involved in semiconductor design and facilitate them to achieve turnover of more than Rs.1500 Crore in 5 years.
- Eligibility:
- Domestic companies, startups, and MSMEs involved in semiconductor design or linked design.
- Approved applicants must maintain their domestic status for three years.
- An applicant must meet threshold criteria to be eligible for disbursement of incentive for the year under consideration.
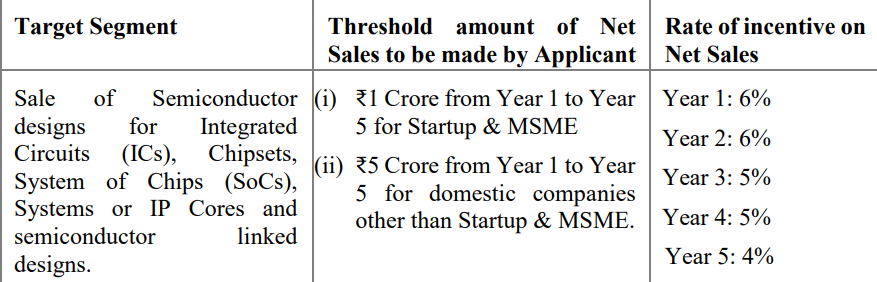
Threshold criteria
|
- In case the Net sales do not meet the threshold amount for any given year, the applicant shall not be eligible for an incentive in that particular year.
- However, the applicant will not be restricted from claiming incentive in subsequent years during the tenure of the Scheme, provided threshold criteria are met for such subsequent years.
Components under DLI
The scheme has three components.
- Chip Design infrastructure support: Under this, C-DAC will set up the India Chip Centre.
- Product Design Linked Incentive.
- Deployment Linked Incentive.

Objectives
- Nurturing and facilitating the growth of domestic companies, startups and MSMEs.
- Achieving significant indigenisation in semiconductor content, thereby facilitating import substitution and value addition in the electronics sector.
- Strengthening and facilitating access to semiconductor design infrastructure for startups and MSMEs.
Issues with the Scheme
- Domestic Status and Foreign Direct Investment: Beneficiary start-ups must maintain domestic status for at least three years after incentives. This limits the scope of foreign direct investment.
- Viable nature of the Semiconductor industry: Start-ups in semiconductor design incur substantial costs with longer-term returns. Further, coupled with the challenges in the funding landscape in India, it reduces investor risk appetite, hindering growth.
- The conflicting role of the C-DAC: C-DAC itself is a market player in chip design, and concerns arise about conflict of interest, capacity, and suitability for implementation and regulation.
Way forward
- Revise the Domestic status objectives: Allow any entity registered in India to engage in the design process.
- The C-DAC as the nodal agency for the DLI scheme necessitates reconsideration: The Karnataka government’s Semiconductor Fabless Accelerator Lab can be made as the implementing agency under the India Semiconductor Mission.
What is a semiconductor?
Applications of semiconductors in daily life
India Semiconductor Mission(ISM)
Components of ISM
Global Scenario
India’s History
Current status
Progress in semiconductor manufacturing
What is ailing India’s Semiconductor Industry?
Initiatives in India
Way Forward
|
For details on the Significance of domestic manufacturing of semiconductors, visit >Significance of domestic manufacturing of semiconductors.





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)