ASER Report 2023
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
- Context (IE | IE): Annual Status of Education Report (ASER) 2023 ‘Beyond Basics’ survey results show foundation skills among 14- to 18-year-olds remain poor.
- Since 2005, Pratham’s Annual Status of Education Report has been tracking school-related trends in rural areas for children aged 6-14.
- In 2023, survey shifted focus to 14-to-18-year-olds. It examined their practical application of reading and math skills, aspirations, and access to digital technology, focusing on their proficiency in using it.
Key findings from the survey
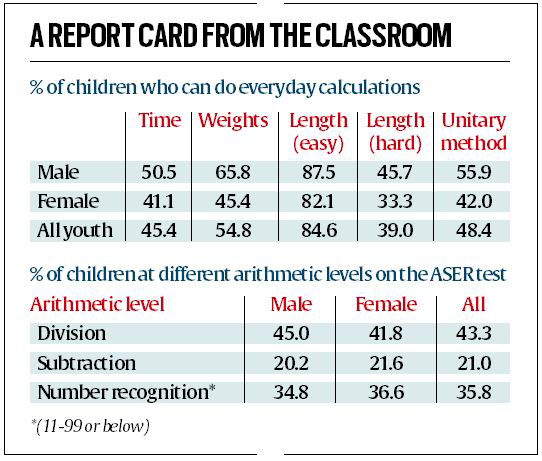
- Reading: 25% of children aged 14-18 struggle to fluently read a Standard II-level text in their regional language. Girls outperform boys across enrollment categories in this aspect.
- Basic Numeracy: Over 50% of 14- to 18-year-old rural children in India face challenges in solving basic three-digit division problems, typically taught in Classes 3-4. They also encounter difficulties in everyday skills such as telling time and basic calculations.
- Digital Skills & Access: Everyone had the basic knowledge of using digital tools. However, they primarily interact with social media.
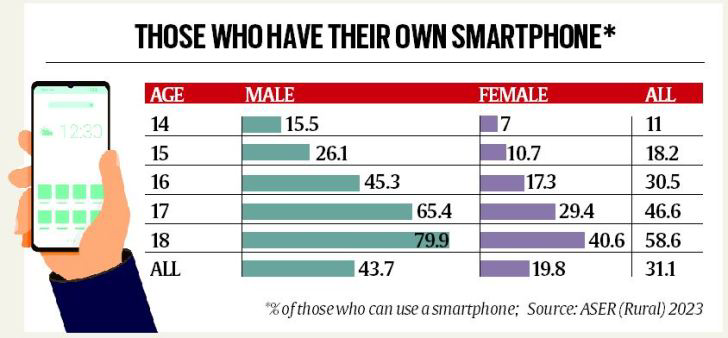
- Aspiration: Over 55% were enrolled in Arts/Humanities, 31.7% in STEM, and 9.4% in Commerce.
- Around 30% are already working, often for their parents. However, they don’t want to continue the same work in future.








![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)