
UN-REDD, REDD+, Short-Lived Climate Pollutants, GCCA+
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
Last updated on April 22, 2024 11:32 PM
UN-REDD and REDD+
| UN-REDD | REDD+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
- In addition to the UN-REDD Programme, other initiatives assisting countries that are engaged in REDD+ include the World Bank’s Forest Carbon Partnership Facility, the Global Environment Facility, the Green Climate Fund etc.
Q3. Which of the following statements is/are correct?
Proper design and effective implementation of UN-REDD+ Programme can significantly contribute to
- protection of biodiversity
- resilience of forest ecosystems
- poverty reduction
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
- Poverty reduction is nowhere mentioned in the REDD+. But the question is not asking for specific details “UN-REDD+ Programme can significantly contribute to?”
- Conservation, sustainable management of forests and enhancement of forest carbon stocks in developing countries will certainly contribute to employment opportunities and help in poverty reduction.
- http://www.fao.org/redd/en/ also says the same “REDD+ can also contribute to achieving other SDGs – including those which address poverty reduction, health and well-being, hunger alleviation, and improving institutions”
Answer: a) 1, 2 and 3 (UPSC Official Key)
Forest Carbon Partnership Facility
- It is a global partnership of governments, businesses, civil society, and Indigenous Peoples focused on reducing emissions from deforestation and forest degradation, forest carbon stock conservation, the sustainable management of forests, and the enhancement of forest carbon stocks in developing countries (activities commonly referred to as REDD+).
- The World Bank assumes the functions of trustee and secretariat.
- The World Bank, the Inter-American Development Bank and United Nations Development Programme are Delivery Partners under the Readiness Fund and responsible for providing REDD+ readiness support.
Objectives
- To assist countries in their REDD+ efforts by providing them with financial and technical assistance.
- To pilot a performance-based payment system for REDD+ activities.
- To test ways to sustain or enhance livelihoods of local communities and to conserve biodiversity.
- To disseminate broadly the knowledge gained in Emission Reductions Programs (ERPs).
Q. With reference to ‘Forest Carbon Partnership Facility’, which of the following statements is/are correct?
- It is global partnership of governments, businesses, civil society and indigenous peoples.
- It provides financial aid to universities, individual scientists and institutions involved in scientific forestry research to develop eco-friendly and climate adaptation technologies for sustainable forest management.
- It assists the countries in their ‘REDD+ (Reducing Emission from Deforestation and Forest Degradation+)’ efforts by providing them with financial and technical assistance.
Select the correct answer using the code given below
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
- It provides financial incentives to countries in their REDD+ efforts. There is no mention of assistance to universities, scientists…
Answer: c) 1 and 3 only
Climate and Clean Air Coalition (CCAC)
- 2012: a few nations, along with the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), came together to form the Climate & Clean Air Coalition.
- It is a partnership of governments, public and private sector, scientific institutions, civil society organizations, etc. committed to protecting the climate through actions to reduce short-lived climate pollutants.
Short-lived climate pollutants (SLCPs)
- SLCPs have relatively short lifetime in the atmosphere – a few days to a few decades.
- Though short-lived, their potential to warm the atmosphere can be many times greater than CO2.
- SLCPs are responsible for up to 45% of current global warming, only next to CO2.
- SLCPs include black carbon, methane, tropospheric ozone, and hydrofluorocarbons.
Black carbon
- It is a major component of soot and is produced by incomplete combustion of fossil fuel and biomass.
- It is emitted from diesel cars and trucks, ships, residential stoves, forest fires, agricultural open burning, etc.
- Its Global Warming Potential is 460-1500 times stronger than CO2.
- Its lifetime varies from a few days to a few weeks.
- When deposited on ice and snow, black carbon causes an increase of melting rate.
- It also influences cloud formation and impacts regional circulation and rainfall patterns and also has negative effect on the photosynthesis.
Methane (CH4)
- Methane is a greenhouse gas that is over 21 times more potent than CO2.
- It has an atmospheric lifetime of about 12 years.
- It is produced through the decomposition of plant and animal waste.
- It is also emitted from coal mines, natural gas and oil systems, and landfills.
- Methane is a precursor of tropospheric ozone.
Tropospheric or ground-level ozone (O3)
- Tropospheric ozone is present in the lowest portion of the atmosphere (10–15 km above the ground).
- It has a lifetime of a few days to a few weeks.
- It is not directly emitted but formed by sunlight-driven oxidation of methane, carbon monoxide (CO), non-methane volatile organic compounds (NMVOCs) and nitrogen oxides (NOX).
- Tropospheric ozone is responsible for reductions in crop yields.
Hydrofluorocarbons
- Though HFCs represent a small fraction of current greenhouse gas emissions, their potential to warm the atmosphere is hundreds to thousands of times greater than that of the same given mass of carbon dioxide.
Benefits of Reducing SLCPs
- Reducing methane and black carbon could prevent major crop losses.
- Reducing SLCPs could slow down the warming expected by 2050 by about 0.5 °C.
- SLCPs play an important role in achieving the 2° C target set by the Paris Agreement.
BioCarbon Fund Initiative
- The BioCarbon Fund Initiative for Sustainable Forest Landscapes (ISFL) is a multilateral fund, supported by donor governments and managed by the World Bank.
- It seeks to promote reduced greenhouse gas emissions from the land sector, from deforestation and forest degradation in developing countries (REDD+), and from sustainable agriculture, as well as smarter land-use planning, policies and practices.
Q. ‘BioCarbon Fund Initiative for Sustain-able Forest Landscapes’ is managed by the
- Asian Development Bank
- International Monetary Fund
- United Nations Environment Programme
- World Bank
- Answer: d) World Bank
Global Climate Change Alliance + (GCCA+)
- (GCCA+) is a European Union initiative.
- It helps vulnerable countries on the front line of climate change.
- GCCA+ initiatives help mainly Small Islands Developing States (SIDS) and Least Developed Countries (LDCs) increase their resilience to climate change.
- It also supports these group of countries in implementing their commitments resulting from the 2015 Paris Agreement on Climate Change (COP21).
Q. With reference to ‘Global Climate Change Alliance’, which of the following statements is/are correct?
- It is an initiative of the European Union.
- It provides technical and financial support to targeted developing countries to integrate climate change into their development policies and budgets.
- It is coordinated by World Resources Institute (WRI) and World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD).
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Answer: a) 1 and 2 only
Arctic Council
- Arctic Council is an intergovernmental forum promoting cooperation, coordination and interaction among the Arctic states, Arctic Indigenous communities and other Arctic inhabitants on common Arctic issues, in particular on issues of sustainable development and environmental protection in the Arctic.
- The Arctic Council consists of the eight Arctic States: Canada, the Kingdom of Denmark (including Greenland and the Faroe Islands), Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia, Sweden and the United States.
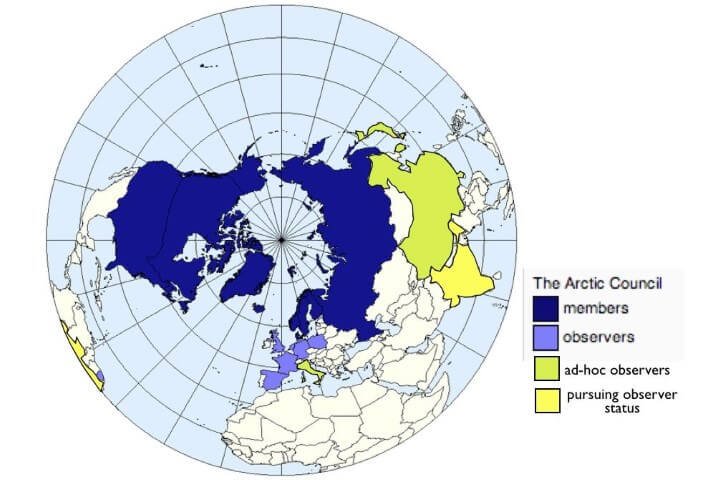
Q. Consider the following countries:
- Denmark
- Japan
- Russian Federation
- United Kingdom
- United States of America
Which of the above are the members of the ‘Arctic Council’?
- 1, 2 and 3
- 2, 3 and 4
- 1, 4 and 5
- 1, 3 and 5
Answer: d)
Last updated on April 22, 2024 11:32 PM















Sir, very very helpful notes.
Thank you very much sir. Very helpful notes