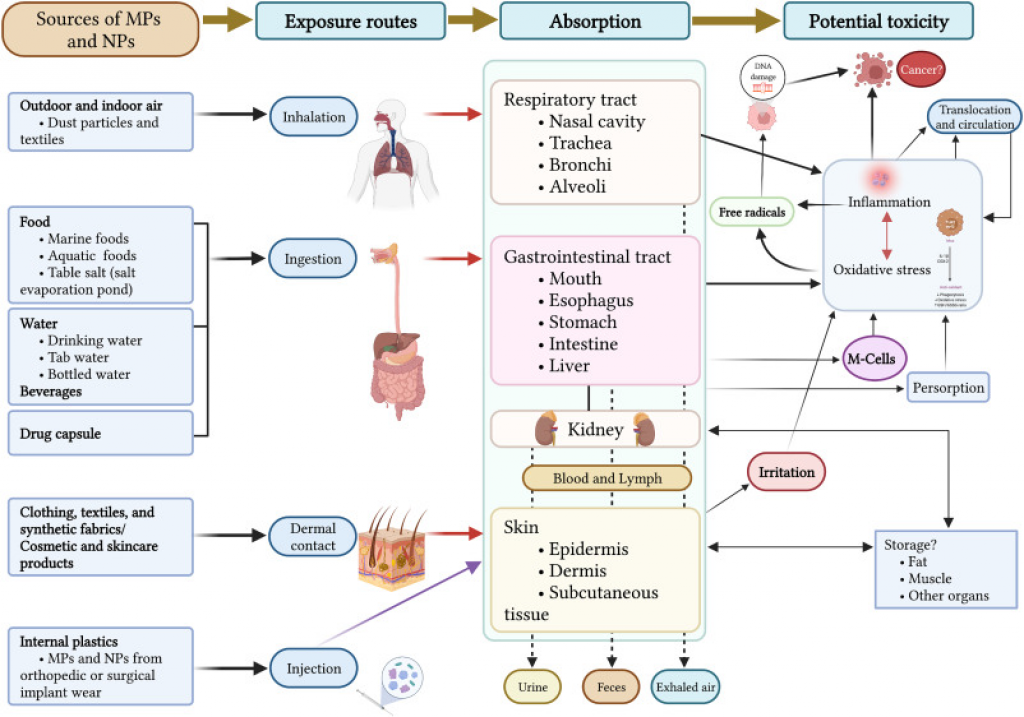
Kaleshwaram Lift Irrigation Project (KLIP)
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
- Context (TH): Telangana Chief Minister called for an inquiry into irregularities in the Kaleshwaram Lift Irrigation Project (KLIP).
- Issues of submerging piers at the Medigadda barrage and the seepage in the Annaram barrage have brought the project into the limelight.
- KLIP is a multi-purpose lift irrigation project in Telangana redesigned from the Pranahita-Chevella project of erstwhile Andhra Pradesh.
- It is constructed on the Godavari River in Kaleshwaram, Bhupalpally, Telangana, India.
- As of now, it is the world’s largest multi-stage lift irrigation project.
- It is unique in terms of its reverse pumping mechanism.
Godavari Basin
|
Components of KLIP
- It is divided into 7 links and 28 packages through 13 districts along with a canal network.
- It targets sourcing a total of 240 TMC (195 from Medigadda Barrage, 20 from the Sripada Yellampalli project, and 25 from groundwater).
- A barrage is constructed at Medigadda, and the water is reverse-pumped into the main Godavari river and diverted through lifts and pumps into a huge and complex system of reservoirs, water tunnels, pipelines, and canals.
- It envisages four major pumping facilities to manage the project’s outflow. The largest is at Ramadugu and Medaram, Annaram, and Sundilla being the others.



Interlinking of Rivers (ILRs)
|
Advantages of Kaleshwaram Lift Project
- Water availability: It will provide water for irrigation, Hyderabad municipal water supply, industrial uses, and drinking water supply to nearby villages.
- Groundwater level restoration: It will replace the use of groundwater in irrigation with canal water.
- Water Recharge Projects: Mission Kakatiya and Mission Bhagirath for water conservation will also be augmented by water supplied through the KLIP.
- Interstate Water Dispute Resolution: A newly signed agreement between Telangana and Maharastra will address the long-standing interstate river water sharing dispute.
- Improvement in Socio-economic Conditions: Farmers and cultivators around the area are expected to benefit from better irrigation, commercial crop cultivation, and a reduction in the cost of agriculture.
Issues in Kaleshwaram Lift Project
- Impact on Agriculture: Submergence of agricultural areas (especially Chilli cultivation areas) and the consequent impact on the state’s economy remains a significant issue.
- Reservoir-induced Seismicity: It can create reservoir-induced seismicity similar to the Koyna reservoir in the Satara district, thereby increasing the possibility of a massive earthquake.
- Environmental Issues: Unusual dam orientation parallel to the stream in Mallannasagar may lead to waterlogging and artesian conditions due to a high hydraulic gradient.
- Displacement Issues: It will submerge 19 villages, resulting in huge socio-economic costs.
- Credibility of Estimates: Many experts are challenging the estimated figures of benefits and associated costs of projects.
- Construction Irregularities: Recently surfaced construction and repair issues raise a question about the project’s long-term vision.
Way Forward
- National Dam Safety Authority emphasized complete rehabilitation to avoid any compromises in the Medigadda barrage.
- Rehabilitation and relief package needs to be revisited to resolve the ‘developmental displacement’ issue.
- The project should undertake corrections as being studied by the Anil Jain (Center Water Commission member) committee — appointed by the Ministry of Jal Shakti to study the recent issues in the KLIP- Medigadda barrage.





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)