Hepatitis
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
- Context (TH): Indian Immunologicals (IIL) launched the country’s first indigenously developed Hepatitis A vaccine, ‘Havisure’.
Hepatitis
- Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver.
- The condition can be self-limiting or can progress to chronic hepatitis, which can lead to progressive scarring of the liver (cirrhosis) or liver cancer.
- Causes: Hepatitis viruses are the most common cause of hepatitis. Toxic substances (e.g. alcohol, certain drugs), and autoimmune diseases can also cause hepatitis.
- Symptoms: Acute infection may occur with limited or no symptoms or may include symptoms such as jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes), dark urine, extreme fatigue, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.
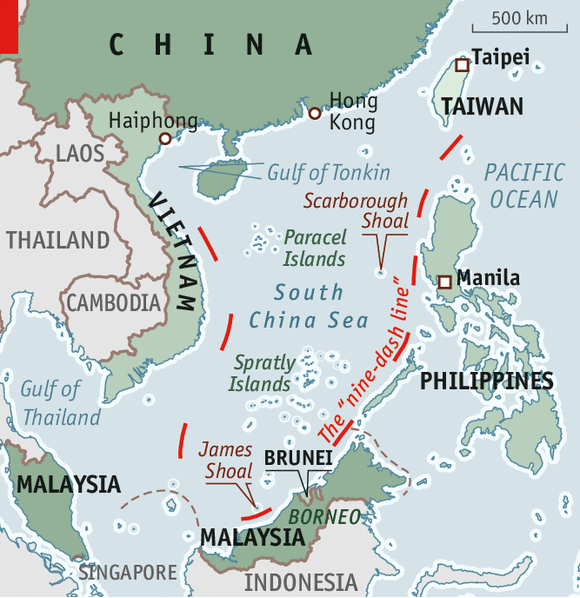
5 Types of Hepatitis Virus
Hepatitis A Virus (HAV)
- It is the most common type of viral hepatitis.
- Causes: It is generally seen in the areas where sanitation and sewage disposal are poor. It is usually a short-term (acute) infection.
- Transmission: Commonly spread through faecal-oral route (ingestion of contaminated food and water). Certain sex practices can also spread HAV.
- Treatment: There is no specific treatment other than using medication. Vaccines are available to prevent HAV.
Hepatitis B Virus (HBV)
- Transmission
- Through exposure to infective blood, semen, and other body fluids.
- From infected mothers to infants at the time of birth
- Through contaminated injections during medical procedures, & through injection drug use.
- Prevention: Safe and effective vaccines are available to prevent HBV.
Hepatitis C Virus (HCV)
- Transmission: Through exposure to infective blood during transfusions of HCV-contaminated blood and blood products, contaminated injections during medical procedures, and through injection drug use. Sexual transmission is also possible but is much less common.
- There is no vaccine for HCV.
Hepatitis D Virus (HDV)
- It occurs only in those who are infected with HBV.
- The dual infection of HDV and HBV can result in a more serious disease and worse outcome.
- Prevention: Hepatitis B vaccines protect from HDV infection.
Hepatitis E Virus (HEV)
- Transmission is mostly through the consumption of contaminated water or food.
- Prevention: Safe and effective vaccines to prevent HEV infection have been developed but are not widely available.
Quick Facts
|





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)