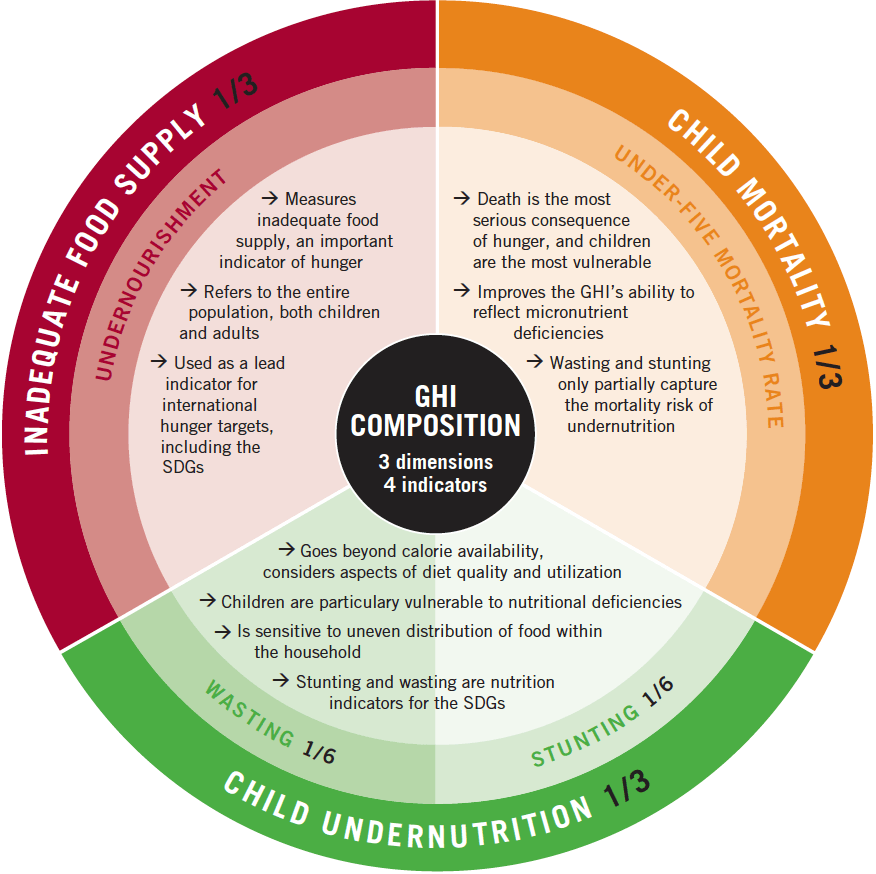
HbA1C test for Diabetes
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
- Context (TH): A nationwide study published in 2023 estimates that India has 10.13 crore people with diabetes and 13.6 crore pre-diabetic people.
- Additionally, over 35% of Indians suffer from hypertension, and nearly 40% have abdominal obesity, both of which are risk factors for diabetes.
- India accounts for 17% of all diabetes patients worldwide.
- The HbA1C test or haemoglobin A1C, is widely used to diagnose pre-diabetes and diabetes, including both type 1 and type 2.
- The HbA1C test, also known as the glycated haemoglobin or glycosylated haemoglobin test, is valuable in managing diabetes effectively.
|
How does the HbA1C test work?
- Sugar from the food you eat enters your bloodstream.
- This sugar, called glucose, attaches to the haemoglobin in your red blood cells.
- Haemoglobin is a protein that carries oxygen to all your body’s cells.
- Everyone has some sugar attached to their haemoglobin. People with pre-diabetes and diabetes have more sugar attached.
- The HbA1C test measures the percentage of red blood cells that have sugar-coated, or glycated, haemoglobin.
Understanding HbA1C Levels
- HbA1C levels are provided as either a percentage or in mmol/mol.
- A higher percentage indicates higher blood glucose levels.
- No diabetes HbA1C levels are below 5.7%.
- Pre-diabetes Levels between 5.7 and 6.4%.
- Diabetes: A percentage of 6.5% or higher.
- In mmol/mol, below 42 corresponds to below 6.0%, 42-47 mmol/mol to 6.0 to 6.4%, and 48 mmol/mol to 6.5% or over.
-
Limitations
- Certain conditions, including kidney or liver failure, severe anaemia, blood disorders, and certain medications, can affect test results.
- Medications like steroids, opiates, or dapsone can also impact results.
- Results may change during early or late pregnancy.
- While the HbA1C test is useful for assessing long-term diabetes control, it’s not universally accepted as a diagnostic test due to assay standardisation issues.
- Doctors may recommend glucose tests alongside HbA1C tests for a clearer diagnosis.
Who needs to take the test and when?
Indian Council of Medical Research’s Guidelines
- For the Management of Type 2 Diabetes (2018), all individuals older than 30 years should be screened for diabetes.
- Those with one or more risk factors, such as obesity, increased waist circumference, history of or treatment for hypertension, history of heart disease, or history of polycystic ovarian syndrome, should be screened earlier.
Retests
- It should be conducted after three years for individuals with normal glucose tolerance.
- If a person is pre-diabetic, retests should be done annually.
- Doctors may recommend more frequent testing, especially for individuals planning to have a baby.
- For those with diabetes, doctors may advise testing every three to six months to monitor blood sugar levels and assess the effectiveness of the treatment plan.
Advantages of HbA1C test over other tests
- Fasting and post-prandial blood sugar tests provide blood sugar levels within a specific time frame. In contrast, the HbA1C test reflects average blood glucose levels over the last two to three months.
- Traditional blood sugar tests may fluctuate based on recent meals and consumption timing. However, the HbA1C test is not affected by these variables, making it more reliable. It can be taken regardless of when the last meal was consumed.
Way forward
- The HbA1C test should not replace other tests for diabetes diagnosis but can be used alongside traditional blood sugar tests.
- Home blood sugar testing is still necessary as it captures fluctuations that the HbA1C test may miss.
- In India, the test may be limited by conditions like thalassaemia, haemoglobin variants, iron deficiency anaemia, and certain medications. Alternative tests are needed in cases where HbA1C levels are affected by these conditions.




![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)