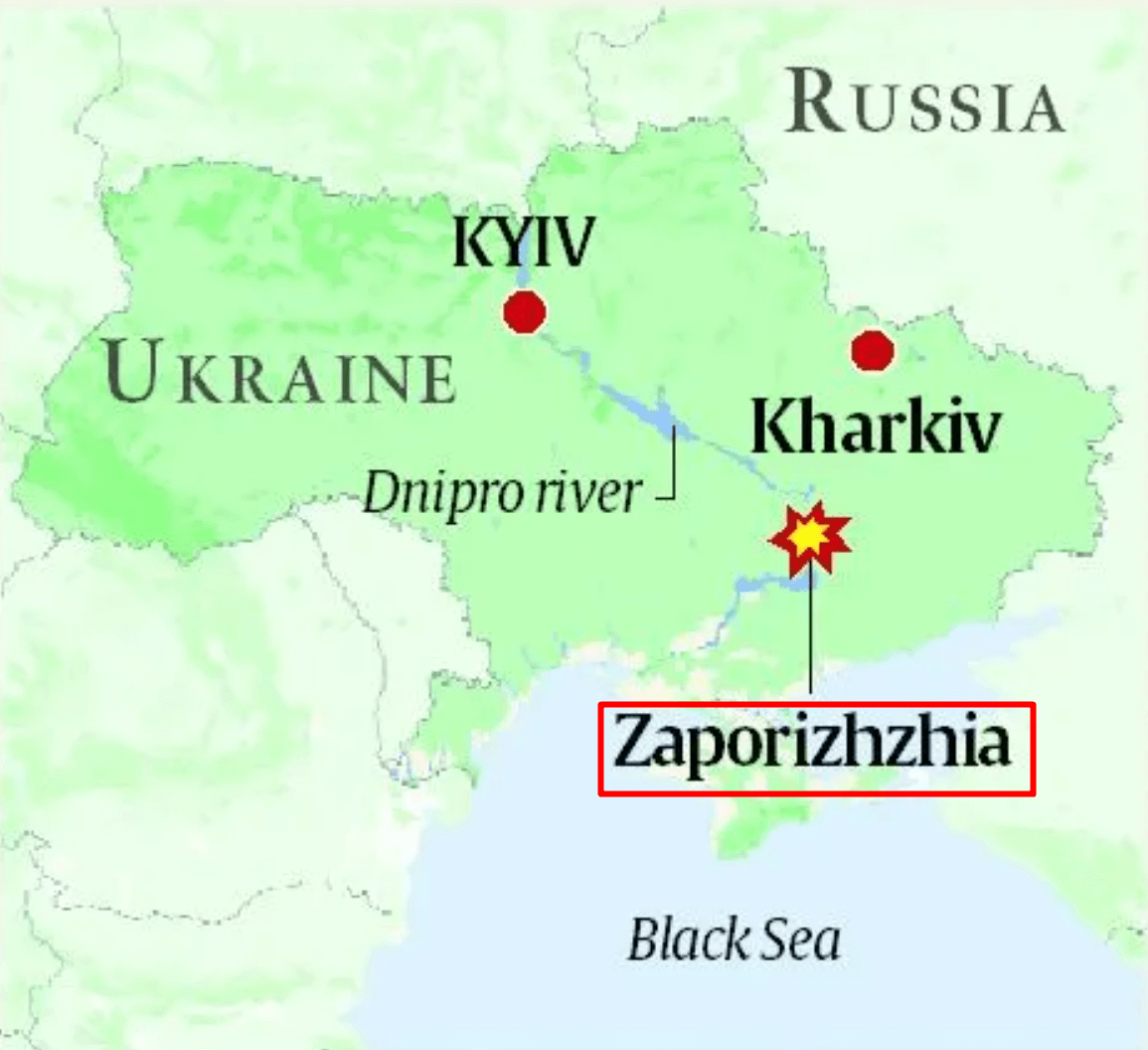
Drone attack on Zaporizhzhia nuclear facility
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
- Context (IE): Zaporizhzhia nuclear facility was attacked again amid the Ukraine-Russia war.
- Zaporizhzhia is one of five nuclear power stations in Ukraine. Russia controls Europe’s largest facility and, for almost two years now, accused Ukraine of attacks.
- The power station has also faced frequent shelling and mortar attacks from both sides, making it the most dangerous nuclear site in the world currently.
- It has six power lines to run, but war has caused disruptions.
Safety of nuclear reactors
Strong but vulnerable
- Most nuclear reactors are made of several layers of steel and concrete and are designed to absorb shocks from earthquakes of magnitude 8 or even higher.
- Ordinary shelling or gunfire can’t impact them seriously. The drone attack did not cause much physical damage to the Zaporizhzhia station.
- However, failure can’t be ruled out in case of a powerful bomb or missile attack.
Risk from power outage
- Nuclear reactors get heated to thousands of degrees Celsius from inside & have to be constantly cooled.
- This is usually done by a circulation of water, which is maintained through an external power source.
- Power outages cause disruptions in it. The failure of power caused the Fukushima disaster of 2011.
- After the Fukushima disaster, several nuclear reactors installed ‘passive’ cooling systems as an additional layer of safety. These systems do not require electricity.
Fukushima disaster of 2011
|
Way forward: Seven Pillars of IAEA for nuclear plant safety
- Physical integrity of facilities must be maintained.
- All safety and security systems and equipment must be fully functional at all times.
- The operating staff must be able to ensure the safety of the facility without undue pressure.
- All nuclear sites must have a secure off-site power supply from the grid.
- There must be uninterrupted logistical supply chains and transportation to and from the sites.
- Effective on-site and off-site radiation monitoring systems, as well as emergency preparedness and response measures, must be implemented.
- There must be reliable communication with the regulator and others.
To know more about Nuclear energy, visit > Nuclear energy.





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)