
Current Affairs for UPSC Civil Services Exam: January 01, 2021
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
[GS2 – Polity – Laws] Medical Termination of Pregnancy (Amendment) Bill, 2020
TH | Prelims + Mains | GS2 > Government policies for development in various sectors and issues arising out of implementation.
- Context: Delhi HC has directed AIIMS to constitute a medical board to examine the condition of a 25-week pregnant woman.
- According to the plea, the foetus inside the woman at the gestational age of 25 weeks suffered from Bilateral Renal Agenesis (both kidneys absent).
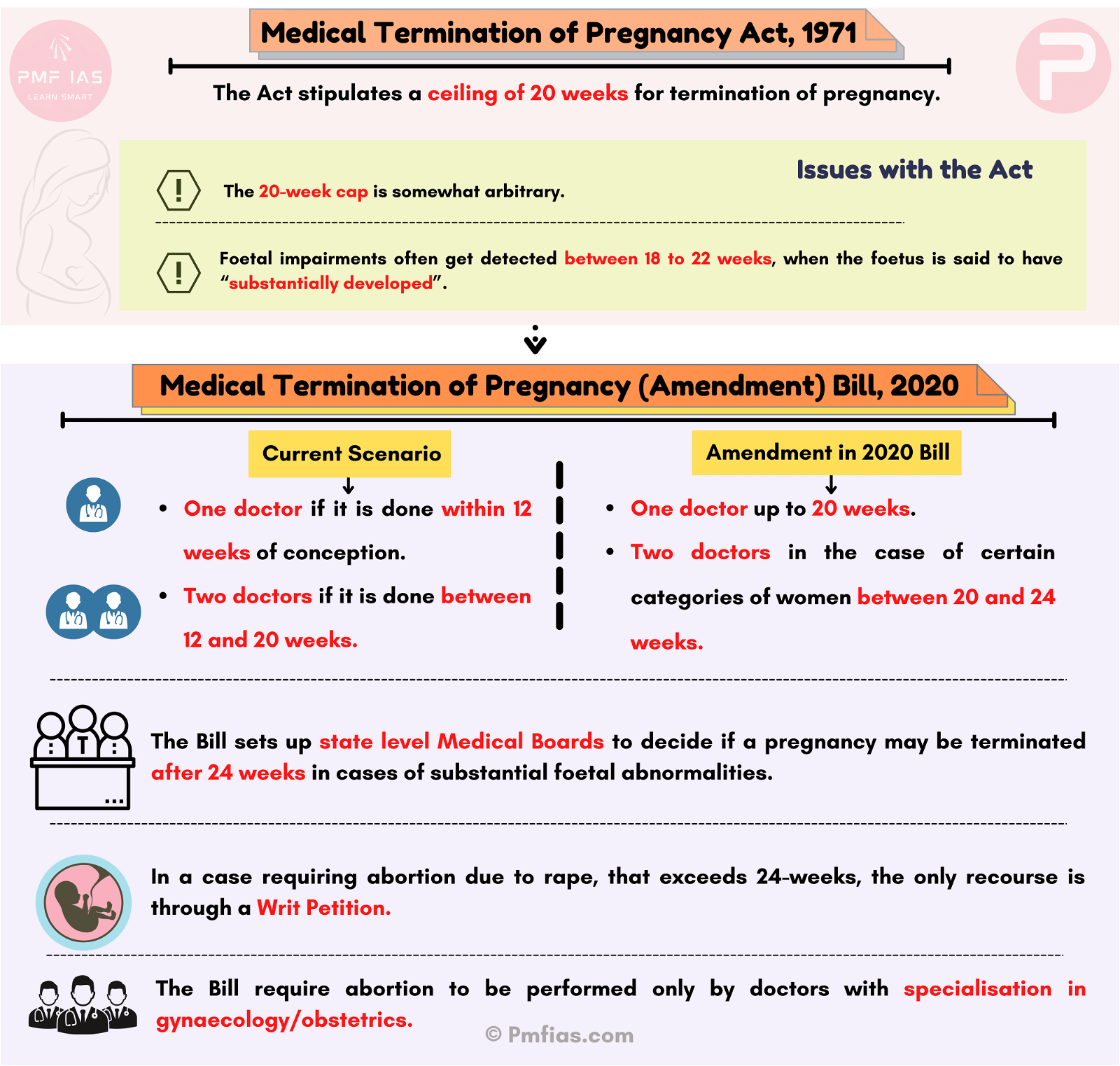
The Medical Termination of Pregnancy Act, 1971
- The Medical Termination of Pregnancy Act stipulates a ceiling of 20 weeks for termination of pregnancy.
- Beyond the 20 weeks period, abortion of a foetus is statutorily impermissible.
Things that medical practitioners need to evaluate while advising an abortion
- Whether continuing with the pregnancy would involve a risk to the life of the mother or cause grave injury to her physical and mental health.
- Whether there would be a substantial risk of the child being handicapped by physical or mental abnormalities.
- If any of these medical eventualities is likely to arise, then the mother’s actual or foreseeable environment (mental & physical state) must also be taken into consideration.
Issues with the act
- The 20-week cap is somewhat arbitrary and has drawn rightful criticism.
- Foetal impairments often get detected at the ultrasound done between 18 to 22 weeks, when the foetus is said to have “substantially developed”.
The Medical Termination of Pregnancy (Amendment) Bill, 2020
- The Act regulates the conditions under which a pregnancy may be aborted.
- Currently, abortion requires the opinion of
- one doctor if it is done within 12 weeks of conception and
- two doctors if it is done between 12 and 20 weeks.
- The 2020 Bill allows abortion to be done on the advice of
- one doctor up to 20 weeks, and
- two doctors in the case of certain categories of women between 20 and 24 weeks.
- The Bill sets up state level Medical Boards to decide if a pregnancy may be terminated after 24 weeks in cases of substantial foetal abnormalities.
- In a case requiring abortion due to rape, that exceeds 24-weeks, the only recourse is through a Writ Petition.
- The Bill require abortion to be performed only by doctors with specialisation in gynaecology/obstetrics.
Issues with the 2020 Bill – socio-economic implications are not considered
- There is a 75% shortage of qualified doctors.
- The shortage may continue to limit the access of women to safe abortion services.
- As per the National Health and Family Survey (2015-16), only 53% of abortions are performed by a registered medical doctor and the balance are conducted by a nurse, family member, or self.
Conflicting Ethical Perspectives
- Terminating a pregnancy is the choice of the pregnant woman (reproductive rights).
- The state has an obligation to protect life, and hence should provide for the protection of the foetus.
- Ministry of Health and Family Welfare to SC in 2019: “Women do not have the absolute right to abort”.
- Many countries set a limit on what is called viability–the stage after which the foetus can survive independently outside the woman’s body.
Need for a relook at abortions laws (mains perspective)
- Expecting the presence of two gynaecologists in rural areas to ascertain the need for abortion is irrational.
- POCSO Act requires any person aware of a minor girl’s pregnancy to report her to the police, regardless of the girl’s consent (invasion of privacy public shaming suicides).
- Due to legal complications, doctors refuse to perform abortions on minors unwanted pregnancies.
- Waiting for the medical board’s decision could push the pregnancy beyond the 20-week period.
- For example, HIV-positive rape victim from Bihar was denied abortion when she was 18 weeks pregnant & was forced to give birth as a result of delay by the Patna HC in 2017.
- The boards do not consider the long-term effects of carrying a pregnancy and only allow abortions if there is an immediate risk to the life of the woman women’s right to health not upheld.
[GS2 – Policy – MHUA] GHTC-India for Affordable Urban Housing
TH | Prelims + Mains | Government policies for development in various sectors > Ministry of Housing & Urban Affairs
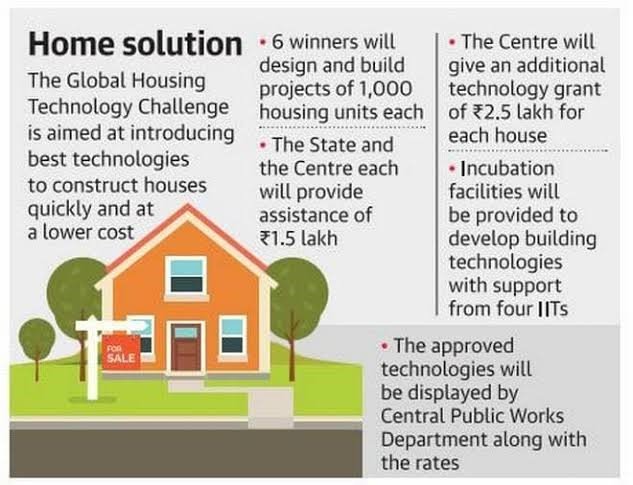
- Launched in 2019, the Global Housing Technology Challenge-India (GHTC-India) is undertaken under the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana Urban (PMAY-U).
- GHTC aims to fast-track the construction & meet the target of constructing 2 crore houses by 2022.
- GHTC focuses on identifying & mainstreaming proven technologies for lighthouse projects.
- It also focuses on spotting potential tech through Affordable Sustainable Housing Accelerators (ASHA).
What are Light house projects?
- LHPs are model housing projects with houses built with shortlisted innovative alternate technology suitable to the geo-climatic & hazard conditions of the region.
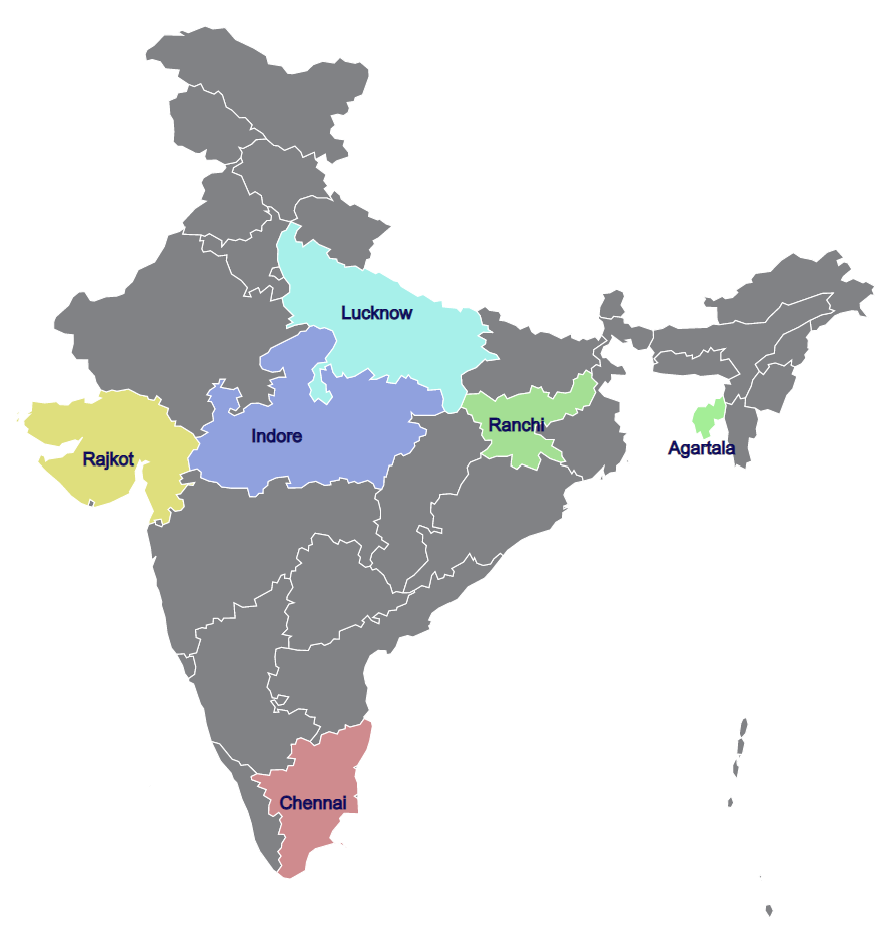
- The LHPs are being constructed at Indore (Madhya Pradesh), Rajkot (Gujarat), Chennai (Tamil Nadu), Ranchi (Jharkhand), Agartala (Tripura) & Lucknow (Uttar Pradesh).
- They comprise about 1000 houses at each location along with allied infrastructure facilities.
- LHPs deliver houses with speed, economy & with better quality of construction in a sustainable manner.
- These LHPs will provide the scope for incubating new technologies for construction & innovation.
- The period of construction is maximum 12 months.
- Approvals will be accorded through a fast-track process by the concerned states (cooperative federalism).
- Six Technology providers have been selected through online bidding process for construction of LHPs.
|
LHP Location |
Technology Selected (names not important; they are just for understanding) |
|
Prefabricated Sandwich Panel System |
|
Monolithic Concrete Construction |
|
Precast Concrete Construction System- Precast components assembled at site |
|
Precast Concrete Construction System-3D Precast Volumetric |
|
Light Gauge Steel Structural System & Pre-engineered Steel Structural System |
|
Stay In-place Formwork System |
| These technologies will be sourced from various developed countries like France, Germany, U.S., etc. | |
Other measures by the government towards affordable housing
- The new Real Estate (Regulation & Development) Act (RERA) is aimed at protecting the buyers.
- Taxes on affordable & regular houses has been reduced from 8 to 1 percent & GST from 12 to 5 per cent.
- Central rental housing complex project was conceived to address the issues faced by migrant labourers.
[GS3 – Envi – CC] Global Warming & Arctic region
IE | Prelims + Mains | GS3 > Environmental Pollution & Degradation | GS3 > Climate Change
Present situation of Arctic
- The region is warming up twice as fast as the global average.
- Since 1980, the volume of Arctic sea ice has declined by as much as 75 per cent.
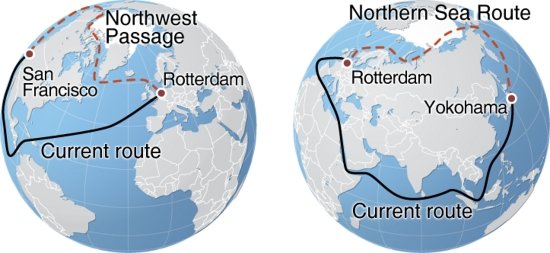
- The Northern Sea Route (NSR) which would connect the North Atlantic to the North Pacific through a short polar arc is slowly opening due to the melting of ice.
- A trickle of commercial cargo vessels has been going through NSR every summer since the last decade.
- Models predict that this route could be ice free in summer by 2050.
Concerns
- The loss of ice & the warming waters will affect sea levels, salinity levels, & current precipitation patterns.
- The Tundra is returning to swamp ( loss of forest loss of carbon sink), the permafrost is thawing ( exposing the subsurface carbon sinks), & wildfires are devastating interior Canada & Russia.
- The phenomenally rich biodiversity of the Arctic region is under serious threat.
New Opportunities
- The opening of the Arctic presents huge commercial & economic opportunities, particularly in shipping, energy, fisheries, & mineral resources.
- Commercial navigation through the NSR is the most tempting: The distance from Rotterdam to Yokohama will be cut by 40 per cent compared to the Suez route.
- Access to unexploited resources
- Unexplored oil & natural gas deposits are estimated to be 22% of the world’s unexplored resources, mostly in the Arctic ocean
- mineral deposits including 25 per cent of the global reserves of rare earths are buried in Greenland.
Challenges associated with new opportunities
- Navigation conditions are dangerous & restricted to the summer.
- Lack of deep-water ports, a need for icebreakers, shortage of workers trained for polar conditions, & high insurance costs add to the difficulties.
- Mining & deep-sea drilling carry massive costs & environmental risks.
- The complication is that, unlike Antarctica, the Arctic is not a global common.
- There is no treaty that governs it, only the UN Convention of Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) deals it.
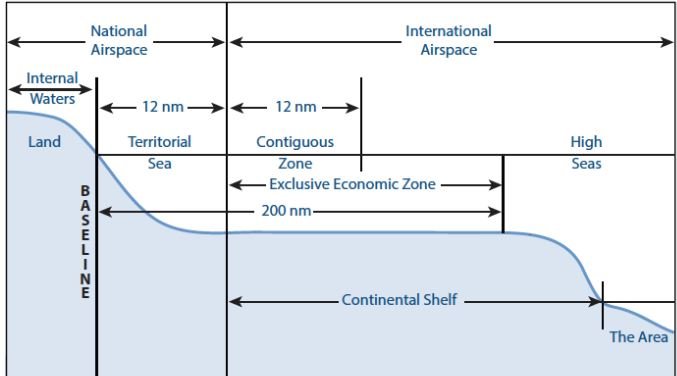
- Large parts of it are under the sovereignty of the five littoral states — Russia, Canada, Norway, Denmark (Greenland) & the US & exploitation of the new resources is well within their rights.
- They have put in overlapping claims for extended continental shelves, & the right to sea-bed resources.
- In 2007, Russia embedded a flag on the seabed below the North Pole to bolster its claim.
- The US, not a party to UNCLOS, is under pressure to strengthen its Arctic presence.
- Russia claiming that the NSR falls within its territorial waters (the US believes it lies in international waters).
- China has been projecting the Polar Silk Road as an extension of the BRI for economic advantage.
Impact on India
- India’s extensive coastline makes us vulnerable to the impact of Arctic warming on ocean currents.
- Research in Arctic melting will help us understand of climatic changes in the Third Pole — the Himalayas.
- The strategic implications of an active China in the Arctic & its growing economic & strategic relationship with Russia are self-evident.
- India has observer status in the Arctic Council, which is the predominant inter-governmental forum for cooperation on the environmental & development (though not the security) aspects of the Arctic.
Previous UPSC Mains Questions
- Why is India taking keen interest in resources of Arctic Region? (2018)
- How does cryosphere affect global climate? (2017)
- What is the economic significance of discovery of oil in the Arctic Sea & its possible environmental consequences? (2015)
[GS3 – Envi – Pollution] Polluters Pay Principle
IE | Mains | GS3 > Environmental Pollution & Degradation
Present situation of Air pollution
- The global death rate attributable to air pollution exposure is 86 deaths per 100,000 people.
- 92% of the population lives in places where air pollution levels are above the WHO guideline for healthy air.
- Of all the deaths caused by ischemic heart disease (the biggest killer), 20% are caused by air pollution.
- Of all the deaths caused by lung cancer (deadliest of all cancers), 19 per cent are due to air pollution.
What is the Polluter Pays Principle?
- The ‘polluter pays’ principle is the commonly accepted practice that those who produce pollution should bear the costs of managing it to prevent damage to human health or the environment.
- For instance, a factory that produces a potentially poisonous substance as a by-product of its activities is usually held responsible for its safe disposal.
- The polluter pays principle is part of a set of broader principles to guide sustainable development worldwide (formally known as the 1992 Rio Declaration).
- When the pollution cost from the release of GHGs is not imposed on emitters, these costs are thus ‘externalised’ to society, representing ‘market failure’.
- Society bears these costs as GHGs are emitted into the atmosphere, which is described a ‘global commons’ as everyone shares & has the right to use.
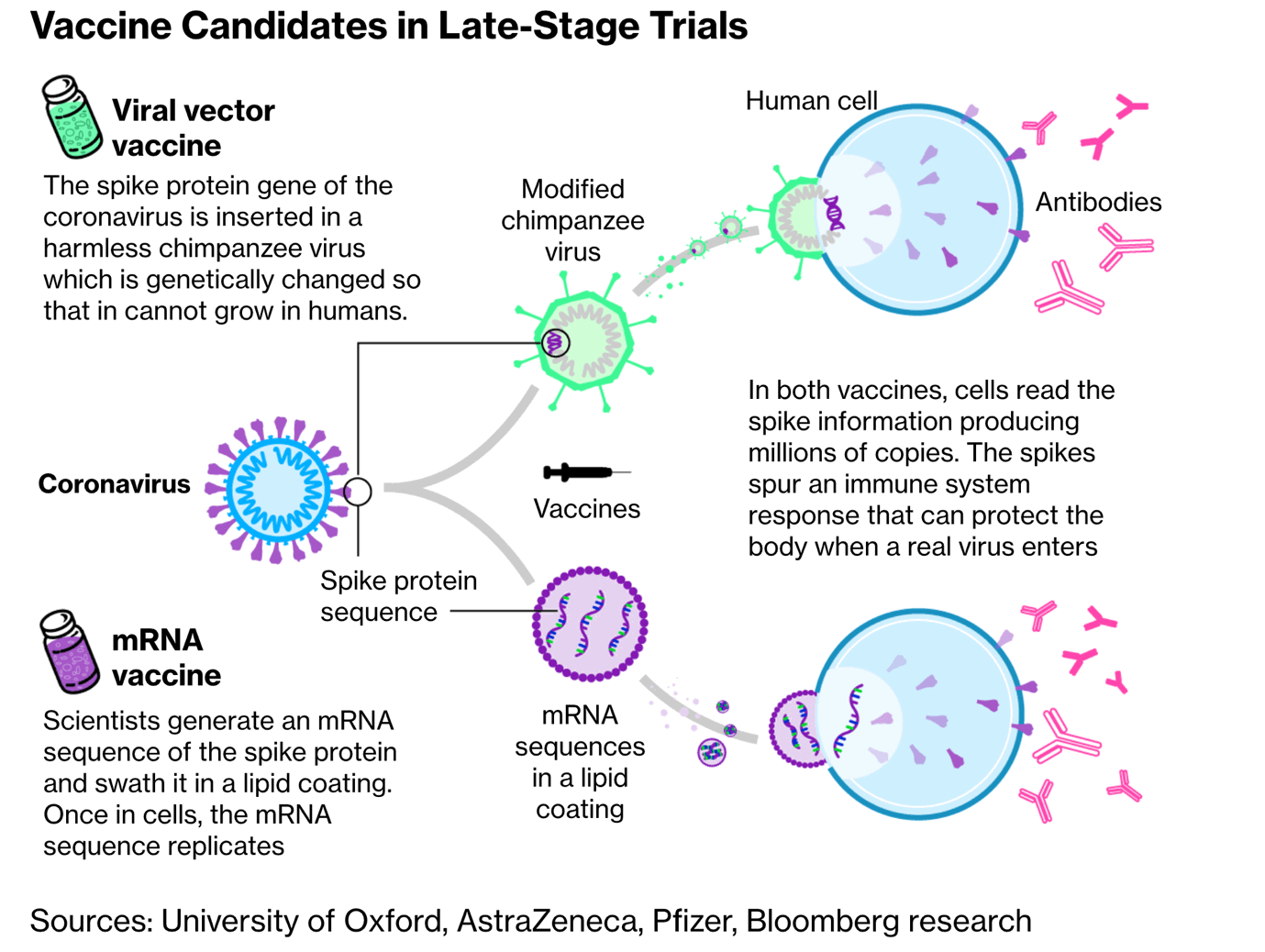
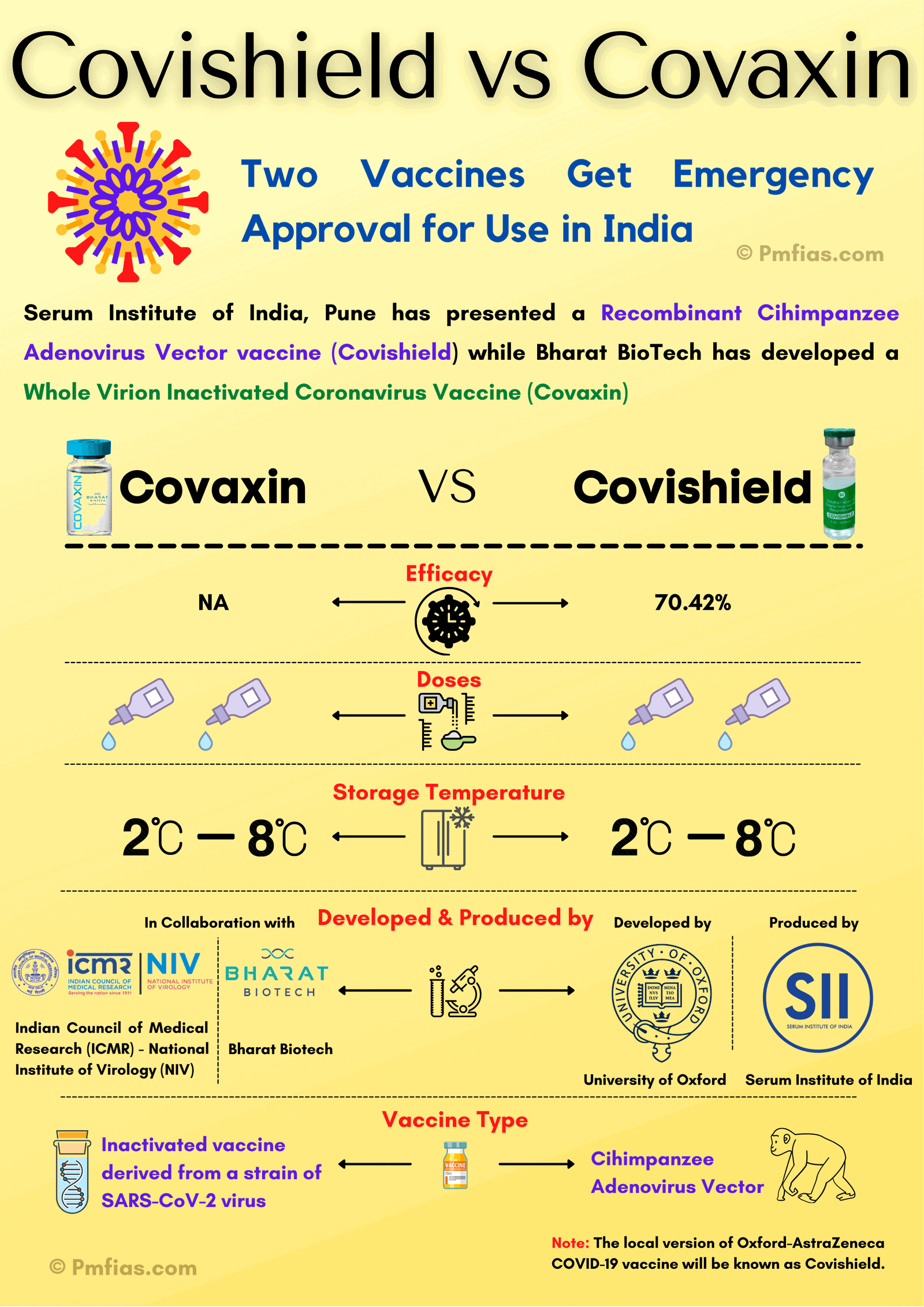
[GS3 – S&T – COVID] COVID-19 Vaccines
PMF | Prelims + Mains
- Context: Pfizer vs Moderna vs Astrazeneca, which is the better vaccine right now for India?
Basics: COVID-19
Which is the Best Vaccine Suited for India?
- Comparing the top three vaccines based on:
Efficacy Rates
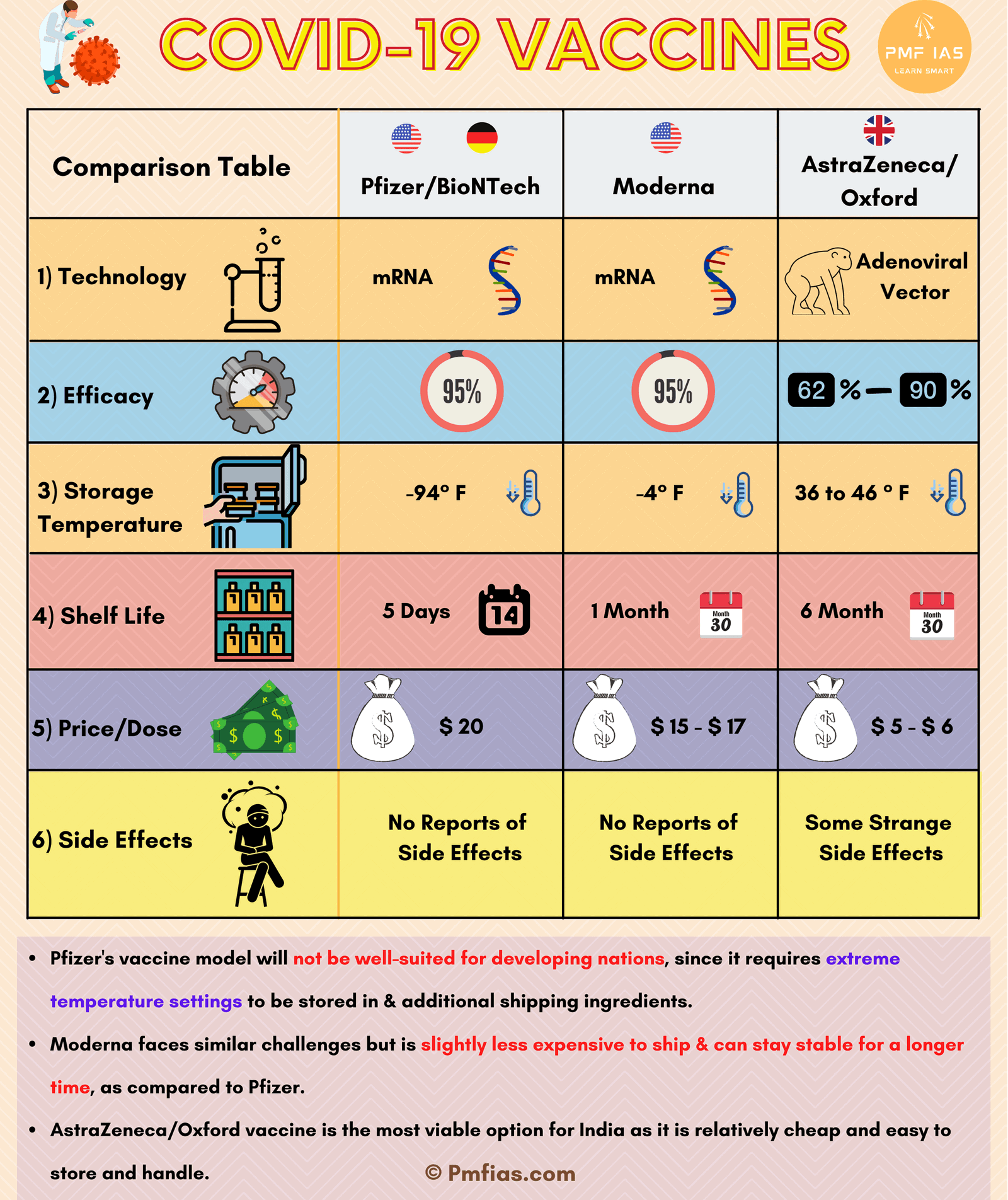
Pricing
- Pfizer’s candidate is the steepest one right now, costing $20 per dose.
- Moderna’s make comes up to cost somewhere around $15-$17 per dose.
- Oxford-Astrazeneca’ shot is by far the cheapest vaccine under offering, as little as $5- $6 (Rs.1000).
Side Effects
- Both Moderna & Pfizer-BionTech haven’t reported the occurrence of undue or alarming side-effects.
- Neither have reports of adverse reactions emerged from people who have been vaccinated right now.
- In comparison to this, the Oxford-Astrazeneca vaccine has been surrounded by controversies in the past months with the many ‘strange’ side-effects being reported from volunteers
Storage & shelf-life
- Storage & shelf-life are prime factors that determine how effective a vaccine would be in real-world settings.
- Many experts claimed that Pfizer’s vaccine model will not be well-suited for developing nations, since it requires extreme temperature settings to be stored in & additional shipping ingredients.
- The vaccine can be stored for use for up to 5 days’ time in a regular refrigerator, for 30 days in a dry-ice freezer, or 6 months’ time in ultra-cold freezers, which are not feasible to arrange everywhere.
- Moderna faces similar challenges but is slightly less expensive to ship & can stay stable for a longer time, as compared to Pfizer.
- Oxford’s dose, wins since it is a vaccine prepared using traditional settings, can be stored for use for longer months, easily delivered & administered.
[GS3 – S&T – ICT] Interconnection Usage Charge (IUC)
TH | Prelims | GS3 > Awareness in the fields of IT, Space, Computers
- Context: Telecom operators not to pay interconnect usage charge from 1st January.
- IUC is a charge payable by a service provider, whose subscriber originates the call, to the service provider in whose network the call terminates.
- This is paid to cover the network usage costs as the operator, on whose network the call terminates, carries the call on its network to the customers.
- IUC is one of the main sources of income for telecom companies.
- In a calling-party pays regime (CPP), if you originate a call, you pay your access provider, who in turn pays termination charges to the network you placed the call.
- The term ‘interconnection’ refers to an arrangement under which telecom players connect their equipment, networks, & services with other Telecom Services Providers.
- TRAI regulates the IUC & addresses the various issues related to interconnection arrangements.
- IUC ensures operators make appropriate investments to carry voice calls without terminations.
TRAI: Telecom Regulator Authority of India
- TRAI is the independent regulator of the telecommunications business in India.
- TRAI was established on 1997 by an Act of Parliament to regulate telecom services & tariffs in India.
- Earlier regulation of telecom services & tariffs was overseen by the Central Government.
- TRAI’s mission is to create & nurture conditions for growth of telecommunications in India to enable the country to have a leading role in the emerging global information society.
- One of its main objectives is to provide a fair & transparent environment that promotes a level playing field & facilitates fair competition in the market.
- TRAI regularly issues orders & directions on various subjects such as tariffs, interconnections, quality of service, Direct to Home (DTH) services & mobile number portability.
[Prelims – Mapping – World] Provinces of Pakistan | Bohai Sea
TH | TH | Mapping for Prelims > World
Provinces of Pakistan
- Context: A Hindu temple was demolished by a mob in the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan.
- Pakistan has four provinces:
- Punjab,
- Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (which now includes the Federally Administered Tribal Areas or FATA),
- Balochistan, &
- Sindh.
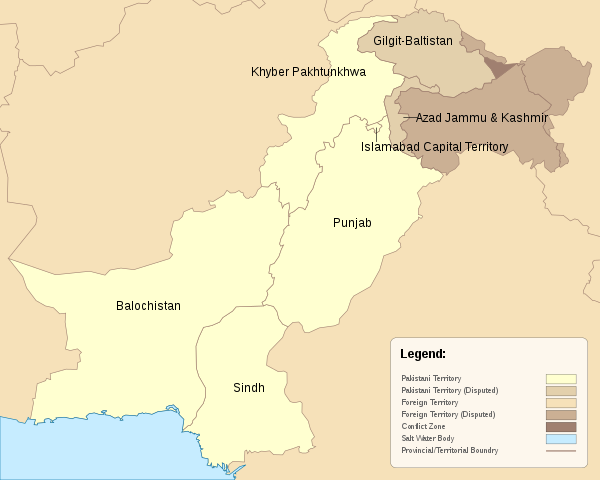
- Though both PoK (Azad Kashmir) & Gilgit–Baltistan are ruled directly from Islamabad, neither is officially listed as the territory of Pakistan.
- They are both considered as “autonomous territories”.
- For India, on the other hand, as per the resolution passed by Parliament in 1994, PoK & Gilgit–Baltistan are both part of the State of Jammu & Kashmir, which is an integral part of India.
- Gilgit–Baltistan is situated on the north-western corner of the Kashmir Valley (trans–Himalayan region).
- This is a picturesque, hilly region to the north of Azad Kashmir & east of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa.
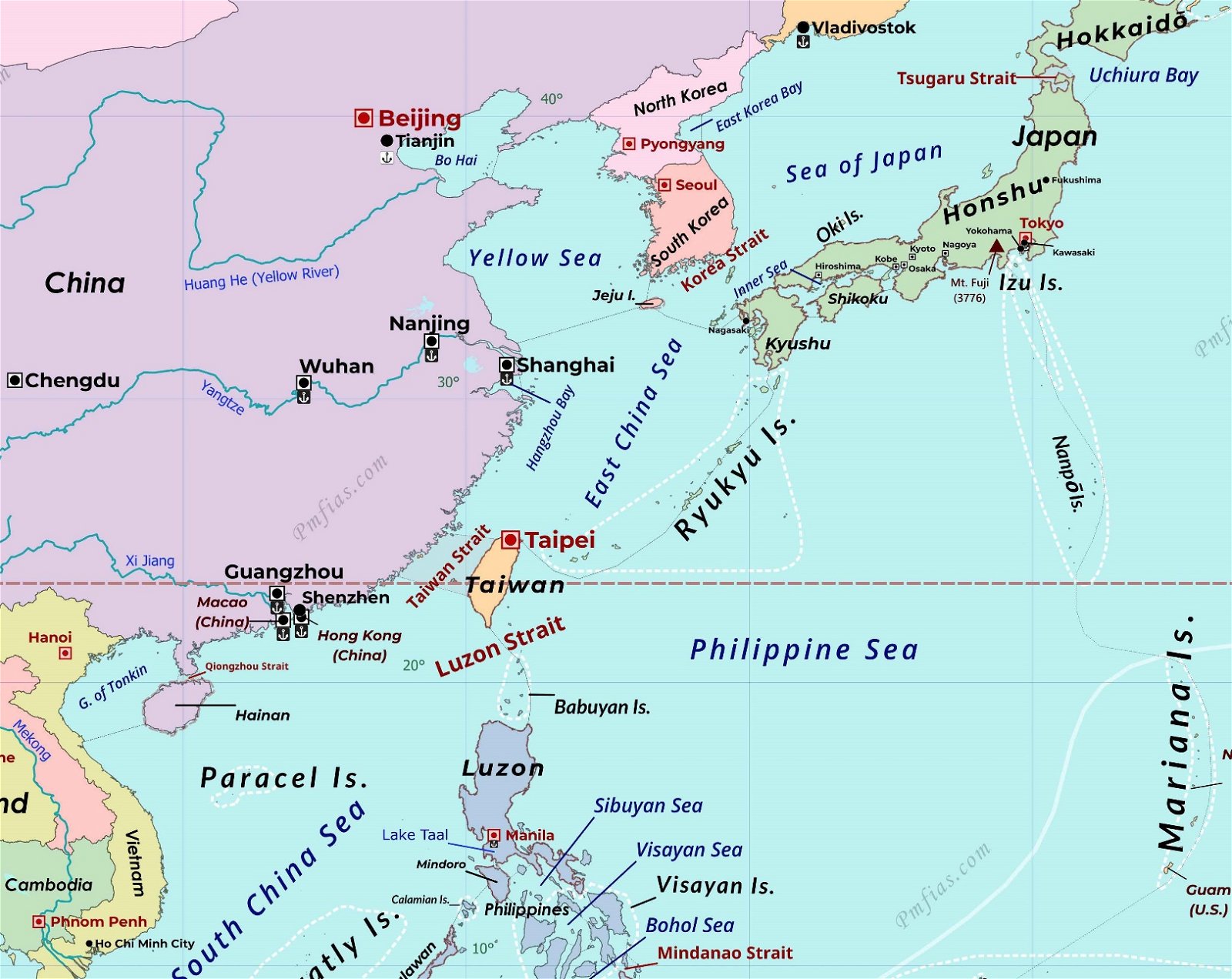
Bo Hai Sea (Bohai Sea)
- Context: India urged China to aid 39 crew members of cargo vessels stranded for months in a port on the Bo Hai Sea (Bohai Sea).
- The Bohai Sea is a marginal sea which is the north-western extension of the Yellow Sea.
- The Bohai Sea is connected to the Yellow Sea via the Bohai Strait.











How can I download these current affairs from jan 2021 ?
Please go through https://www.pmfias.com/current-affairs-upsc-ias-cse/
Will you be providing the other subjects like polity course content as well?
Please reply?
Thankyou!
Yes, all the subjects’ current affairs will be included.
sir these seems informative and a job well done but how do one subscribe and download these notes on daily basis or whatever the criteria is, please let us know asap.
Please go through https://www.pmfias.com/current-affairs-upsc-ias-cse/
How can I download current affairs