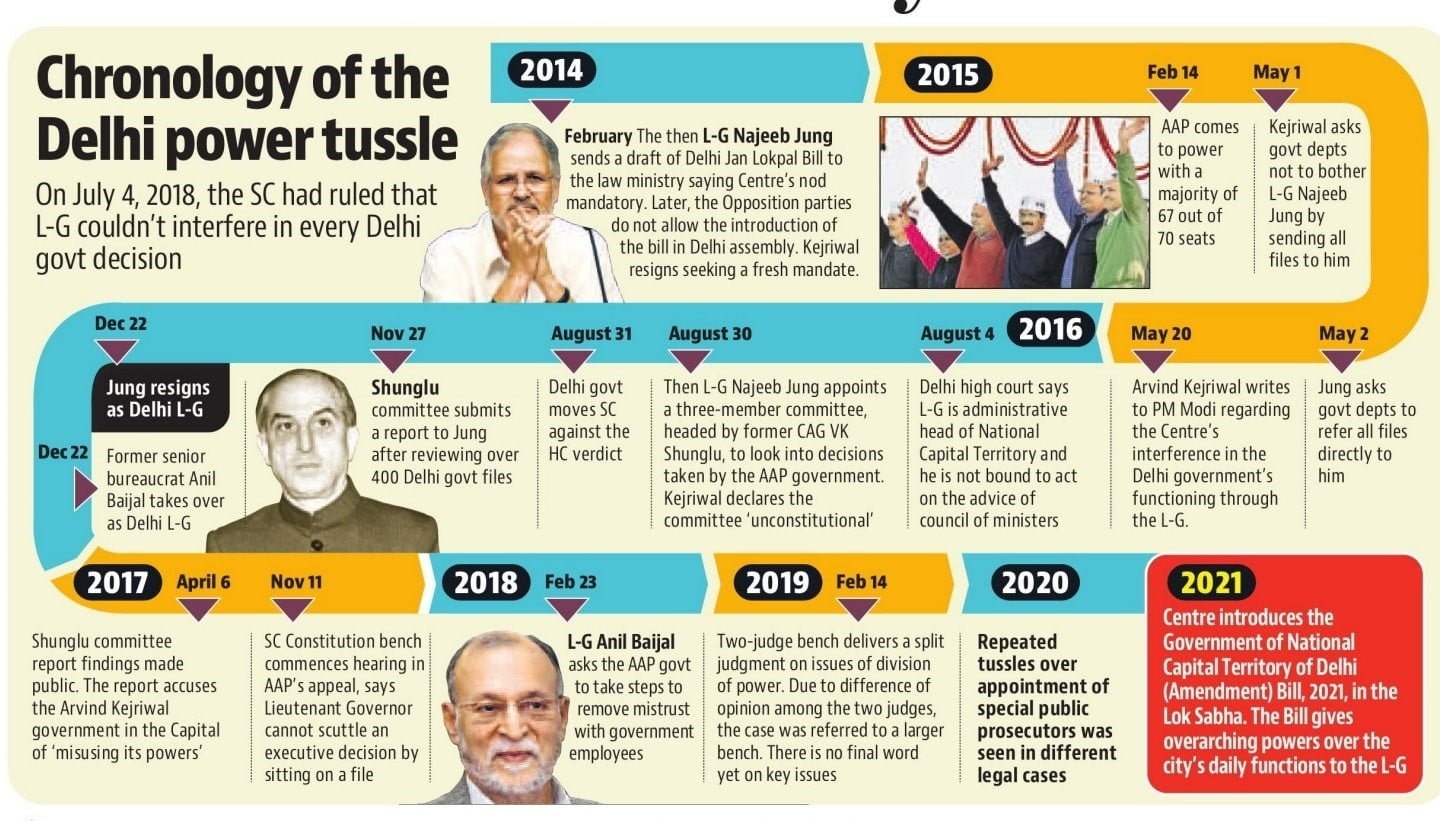
Cryptocurrency and Legal Tender, Cryptocurrency vs. Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC)
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
Cryptocurrency
- Context (TH): IMF’s changed view on the crypto market in Latin America.
- Cryptocurrency, sometimes called crypto-currency or crypto, is any form of currency that exists digitally or virtually and uses cryptography to secure transactions.
- Cryptocurrencies don’t have a central issuing or regulating authority.
- They run on blockchain technology.
- Units of cryptocurrency are created through a process called mining, which involves using computer power to solve complicated mathematical problems that generate coins.
- Bitcoin is the largest cryptocurrency by market capitalisation.
Cryptocurrency and Legal tender
- Few countries have entirely banned crypto assets.
- El Salvador is the first country in the world to adopt Bitcoin as its legal tender.
- In India, Cryptocurrencies are a kind of assets like gold, silver, etc. So, Cryptocurrencies are not a currency. People can transact in cryptocurrencies (Just like GOLD).
- China has banned crypto mining and unregulated virtual assets in the country.
IMF’s stance on cryptocurrency
- IMF was against El Salvador’s move to adopt Bitcoin as legal tender, citing fiscal risks.
- Recently, IMF noted that a crypto ban “may not be effective in the long run” in the region.
- It called for regulation of cryptocurrency and recording crypto transactions for transparency.
RBI’s Stance on Cryptocurrency
- In 2013, RBI issued a circular warning to the public against using virtual currencies.
- In 2018, RBI issues a circular preventing commercial and cooperative banks, payments banks, small finance banks, NBFCs, and payment system providers from dealing in virtual currencies or providing services to all entities which deal with crypto exchanges.
- In 2020, SC declared the 2013 RBI circular unconstitutional.
Budget FY23 and Crypto transactions
- In Budget 2022-23, Government proposed to levy a tax of 30% on the transfer of virtual assets, including NFTS and cryptocurrencies.
- Trades are subjected to a 1% TDS. ie Citizens selling their tokens — Bitcoin, Ethereum, Dogecoin, Solana and others — receive 1 per cent less the value of the assets at the selling price.
Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC)
What is the difference between cryptocurrency and CBDCs?
|




![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)