India-ASEAN FTA Discussions
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
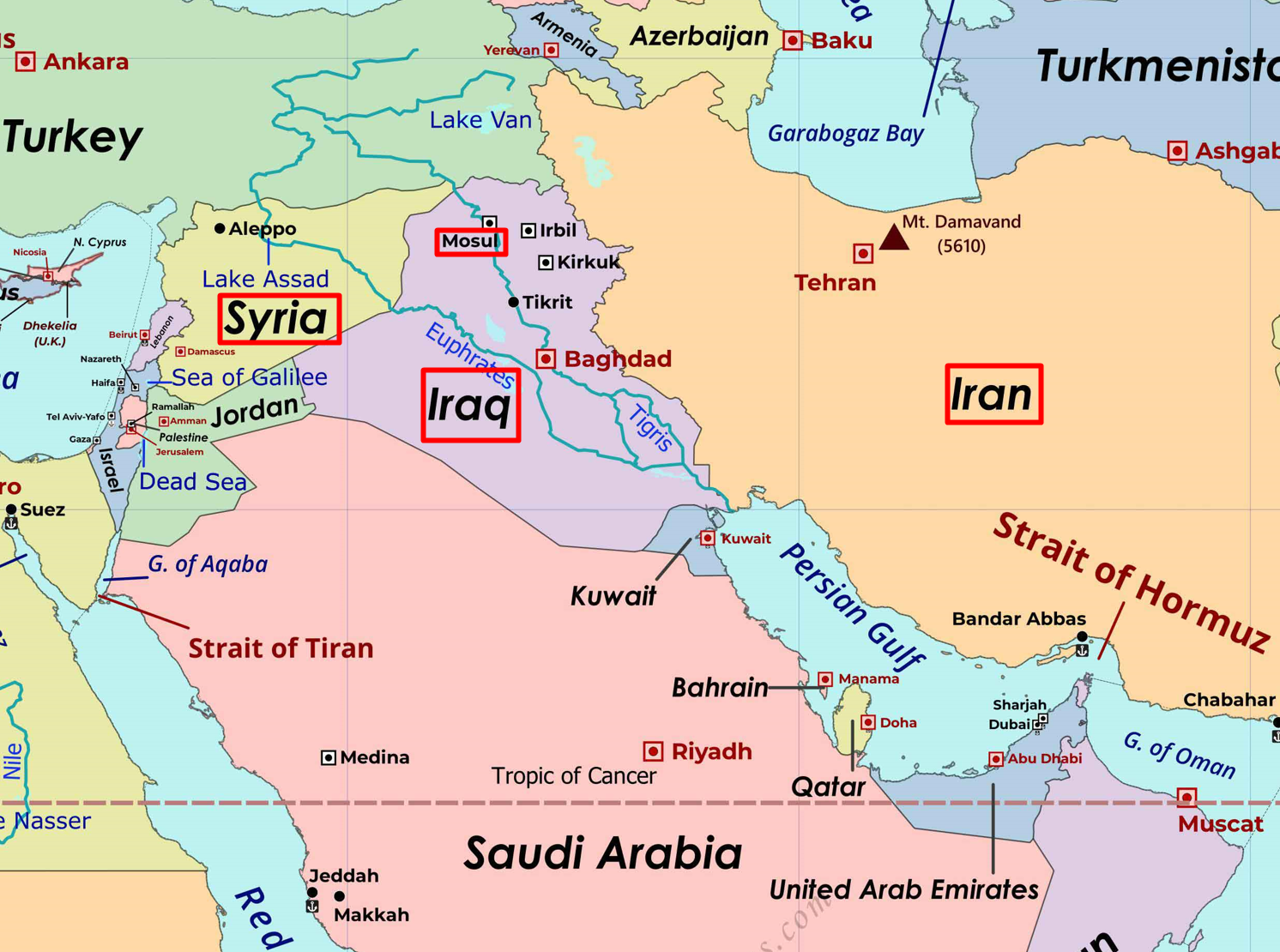
- Context (TH): India and the Association of South East Asian Nations (ASEAN) will begin negotiations to “modernise” the 15-year-old free trade agreement (FTA).
- ASEAN accounted for 11.3% of India’s global trade in 2022-23.
- The ASEAN India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITGA) is expected to be completed by 2025.

Need to Renegotiate FTA
- After the FTA, India’s trade deficit with ASEAN rose from $7.5 billion annually to $43.57 billion in FY23.
- Incidences of re-routing of goods by China through the ASEAN countries cause duty losses.
New Expected Provisions
- New elements of product-specific rules will make FTA more efficient.
- Rules of Origin will be incorporated to increase market access and to stop Chinese circumvention.
- Trade remedies will protect domestic industry against unfair trade practices or unforeseen surges in imports of goods.
- No new areas, such as environment, labour, MSMEs or gender, will be added to avoid new issues.
|
Types of Trade Agreements
- Trade Agreement: Cooperation between two or more countries for specific trade or investment terms.
Free Trade Agreement
- Two or more countries provide preferential trade terms, tariff concession, etc., to the partner country.
- It is more detailed than a Preferential Trade Agreement with a “Negative list” of excluded items.
Preferential Trade Agreement (PTA)
- Preferential right of entry is given by reducing duties on “Positive list” items.
- Tariffs may be reduced to zero for some products, even in a PTA.
- India signed a PTA with Afghanistan.
Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA)
- Besides the above cooperation, CEPA also includes the regulatory aspect of trade.
- India has signed CEPAs with South Korea and Japan.
Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement
- It covers negotiation on trade tariffs and “Tariff Rate Quota” only.
- It is not as comprehensive as CEPA.
- India has signed CECA with Malaysia.
Framework agreement
- Framework agreement primarily defines the scope and provisions of the potential deal.
Early Harvest Scheme
- It is a precursor to an FTA/CECA/CEPA between two trading partners.
- Before the conclusion of the actual FTA, countries identify certain products for tariff liberalisation.





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)