
New Agricultural Practices: Hydroponics, Aquaponics, Aeroponics
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
Last updated on April 16, 2024 6:27 PM
Protected Cultivation of Horticulture Crops
- Protected cultivation practices are cropping techniques wherein the microenvironment is controlled partially/ fully as per plant need during their period of growth to maximize the yield and resource saving.
|
Geoponic |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Green House
- Green houses are climate controlled with cooling and heating system.
- It is mainly used to grow exotic vegetables, off-season growing of vegetables, floriculture, planting material acclimatization and plant breeding and varietals improvement under adverse agro-climatic conditions.
- The degree of sophistication of greenhouses include fully automated systems with poly carbonate sheet roofing (double walled), heating and cooling systems, etc.
Poly House
- Poly house is less sophisticated version of green house with naturally ventilated climate controlled as against the fully climate controlled green houses.
- Usage of poly houses are similar to green houses.
Hydroponics
- Hydroponics is a method of growing plants without soil, using water enriched with balance mineral nutrients essential for plant growth and yield.
- The nutrients and PH level are maintained suiting to the selected crop for better growth.
- With increasing water scarcity due to frequent droughts and declining land availability for farming, government agencies are promoting hydroponic for growing vegetables, fruits and fodder.
Advantages of hydroponics
More yield in a smaller patch of land
- Hydroponics supports vertical farming and is ideal to grow crops in congested urban environment.
- Vertical farming: The plants are grown on raised beds that stand a few feet from the ground, making it possible to cultivate several rows on either side of the bed.
- The increase in output happens because the cropping cycle is reduced, and the plants doesn’t have to grow long roots in search of nutrients.
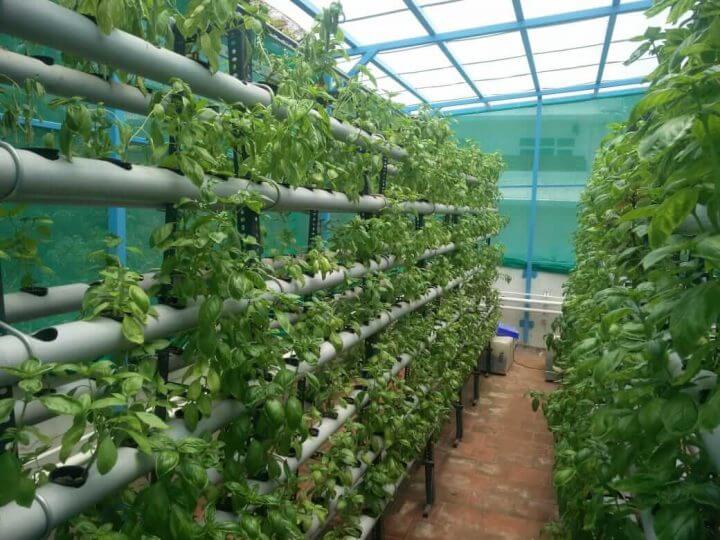

Picture Credits: The Better India
Allows one to tailor crops as per market demand and this reduces wastage
- In hydroponics, cropping cycle is reduced and harvesting times are a lot shorter.
- In traditional farming, sometimes crops grown are not really required in the market at that point of time. This leads to wasted produce.
Significantly reduced water usage yet superior yield
- Hydroponics systems require only around 10 percent of the water that soil-based agriculture requires.
- In traditional farming, water and nutrients are lost in soil. This leads to groundwater contamination.
- In hydroponics, the nutrient solution is mixed into the water and is supplied directly to the roots.
- Since the water directly reaches the roots, it is absorbed much better and nothing is lost in soil absorption.
- The plants are provided with maximum possible nutrients which results in multi-fold growth.
Better quality control and better environment
- Hydroponics reduces both cost on transportation and emissions.
- Hydroponics makes the application of organic farming techniques very simpler.
- Sticky pads and a solar powered insect trap can be used to trap insects. This reduces the use of insecticides.
- Soil-borne diseases and pests are also low as the crops are grown in a closed environment free of soil.
- Also, natural ingredients such as neem oil can be used much more effectively to control pests. This reduces the use of pesticides.
Better nutritional value of crops
- Fodder produced through hydroponics is more nutritional than the regular fodder.
- As food production is closer to the consumer, time is not lost in logistics & hence there is no loss of nutrients.
Better cultivation techniques and application of sci & tech
- The farms can be indoors or outdoors (a greenhouse).
- Suitable for vertical farming under greenhouse conditions and other modified structures.
- Each hydroponic crop can be given a favourable and individual climatic condition through an automated temperature and humidity controlled greenhouse.
- The farm can be managed remotely using the internet of things (IoT – schedule a fertigation session, actively monitor the plants remotely, automated humidity and temperature control, nutrient and input control, etc.).
- The crop can use natural light or artificial lighting (day and night – 24/7 growth period).
Opportunities
- Demand for chemical-free food is increasing with rising awareness among consumers.
- The organic market in India at present is estimated to be $1.3 billion (about Rs 9,000 crore), expected to double by 2021.
- Ministry of Agriculture has subsidy programme for hydroponics.
Disadvantages of Hydroponics
Capital-intensive
- Though hydroponics is typically much cheaper over time, it does require a substantial upfront cost to establish any sort of larger system.
Needs uninterrupted power supply
- Power failure can cause pumps and equipment to stop working.
Lack of awareness
- Many people fear that hydroponics requires substantial know-how and research, when in fact, it’s very similar to traditional gardening.
Aquaponics
- The method combines aquaculture — cultivating fish and other aquatic animals in tanks with organic inputs — with hydroponics, where plants are cultivated in water.
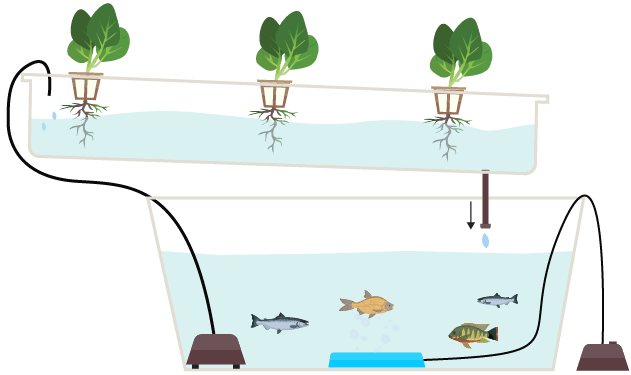
- The water from the fish tank is pumped onto the beds where plants grow.
- While the fish excretions provide nutrients for the plants (hence no chemical fertilizers are needed), the clean water is recirculated back to the fish tank.
- While the initial cost to set up the facility would be high, the recurring cost is low in aquaponics.
- The difference between aquaponics and hydroponics is that synthetic fertilisers are used in hydroponics for providing nutrients to plants and hence cultivation of fish is not possible in hydroponics.
Aeroponics
- Unlike in hydroponics, the roots of plants grown in an aeroponic system are suspended in the air and the spraying of water and nutrients leads to an oxygen-rich, misty environment.
- Aeroponics has been implemented as an alternative to water intensive hydroponic systems worldwide.
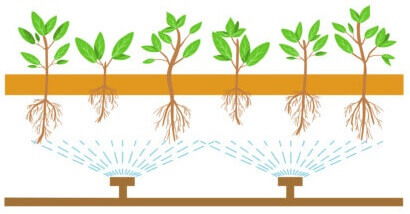
Advantage of aeroponics over hydroponics
- Aeroponics can limit disease transmission since plant-to-plant contact is reduced.
- The enhanced oxygen availability at the root zone leaves disease-causing pathogens dormant.
- Improves uptake of minerals by plants and development of healthy root systems.
- Helps in faster and better growth of plants with a plentiful supply of oxygen, water and nutrients.
- Plants in a true aeroponic conditions have 100% access to the CO2 concentrations for photosynthesis.
- This leads to a multi-fold increase in plant metabolism, which in turn results in a vast increase in production.
- Any species of plants can be grown in a true aeroponic system because the microenvironment of an aeroponic can be finely controlled.
- Aeroponically grown plants have high dry weight biomass (essential minerals).
- According to NASA, aeroponically grown plants require ¼ the nutrient input compared to hydroponics.
- Unlike hydroponically grown plants, aeroponically grown plants will not suffer transplant shock when transplanted to soil.
Last updated on April 16, 2024 6:27 PM












Do you have any information on Training conducted by a Govt Organisation in Hydroponics