Covid-19 Tests: RT-PCR, Rapid Antigen Test & Serological Test
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
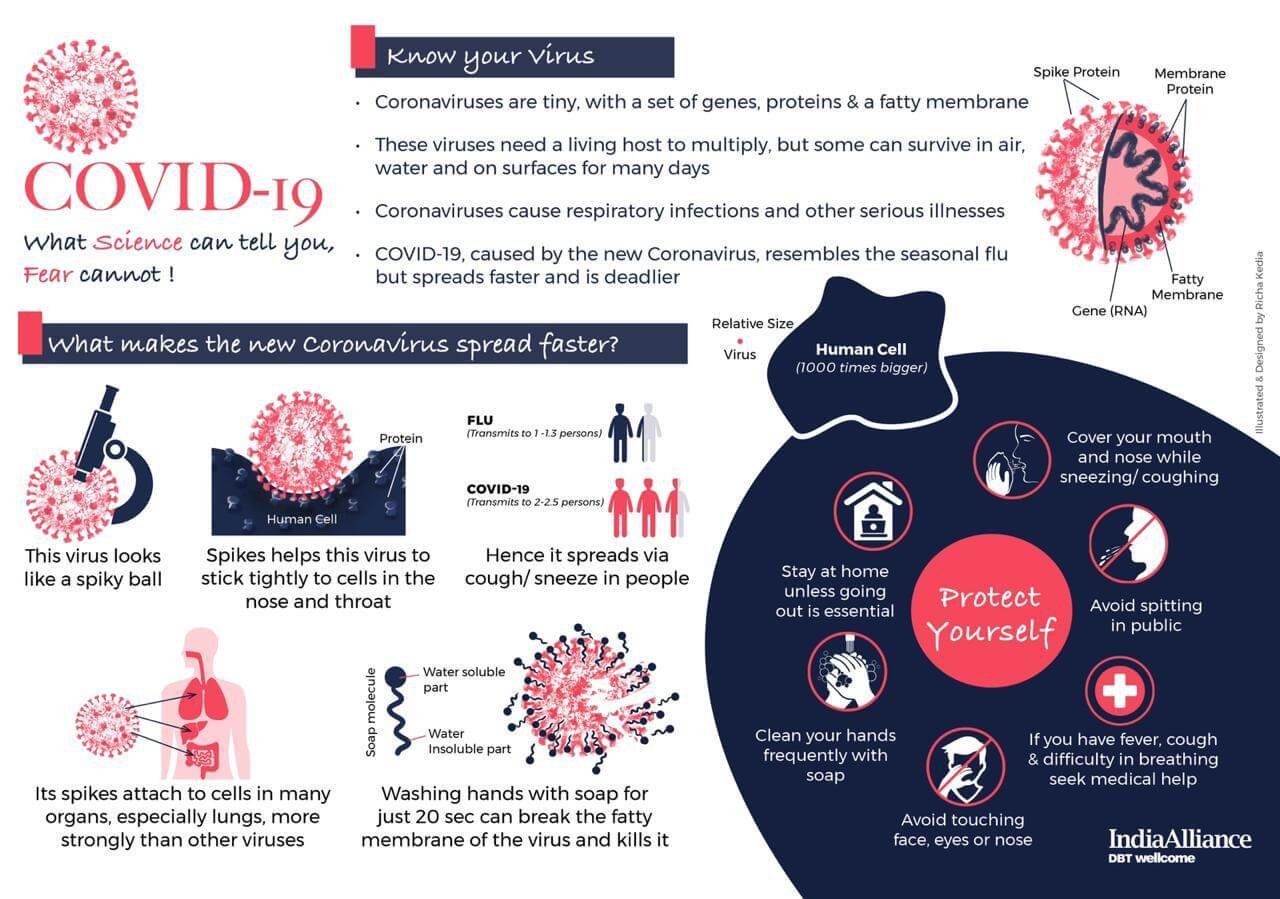
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
- Virus, Difference Between Virus & Bacteria, DNA & RNA Viruses
- Coronavirus, Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19 or 2019-nCoV)
- Immune System, T– Cells & Coronavirus, Cytokine storm
- Covid-19 Tests: RT-PCR, Rapid Antigen Test & Serological Test <===
- Proposed Vaccines, Treatments in the Context of COVID-19
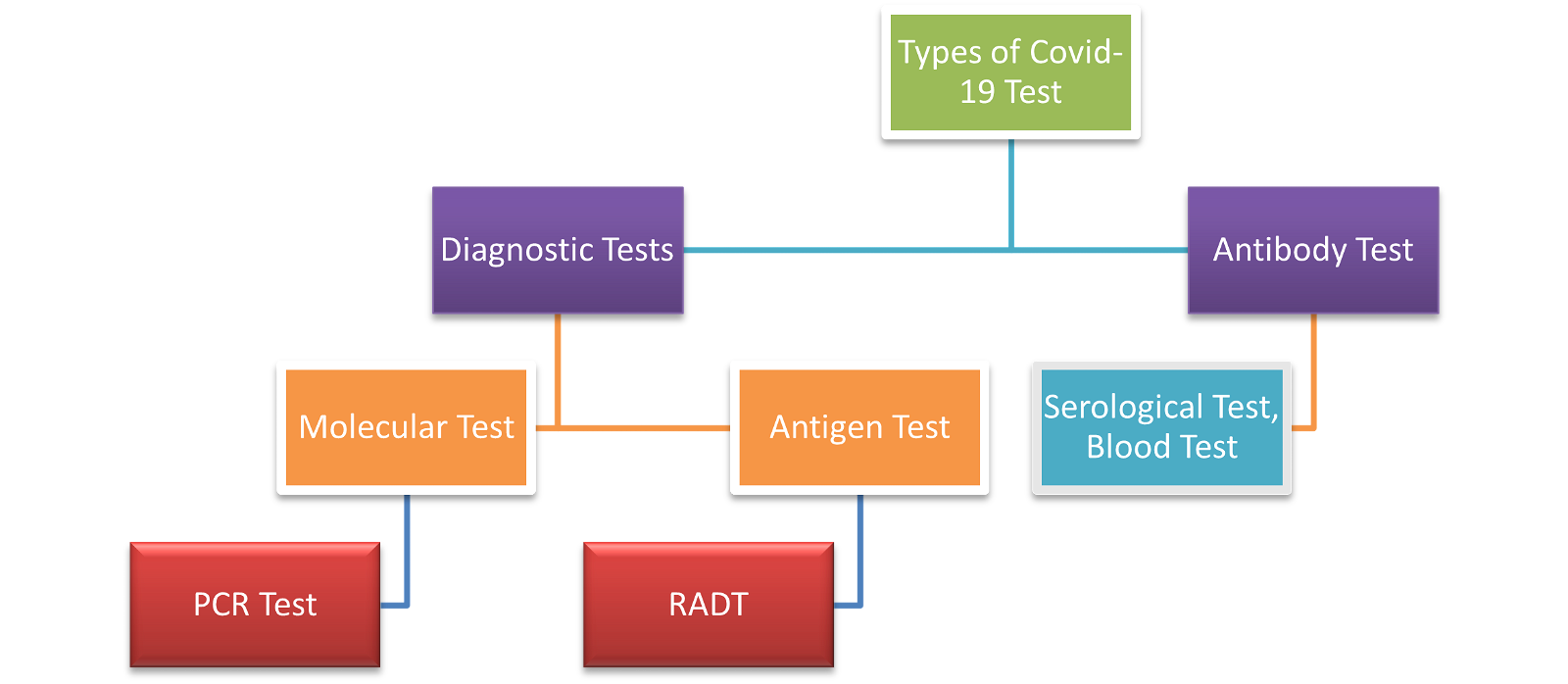
Different Types of Covid-19 Tests
- There are two different types of tests – Diagnostic tests & Antibody tests.
- A diagnostic test can show if you have an active coronavirus infection.
- An antibody test looks for antibodies that are made by your immune system in response to a threat, such as a specific virus.
- Antibodies can help fight infections.
- Antibodies can take several days or weeks to develop after you have an infection & may stay in your blood for several weeks or more after recovery.
- Because of this, antibody tests should not be used to diagnose an active coronavirus infection.
- At this time researchers do not know if the presence of antibodies means that you are immune to the coronavirus in the future.
Link- Source & Credits
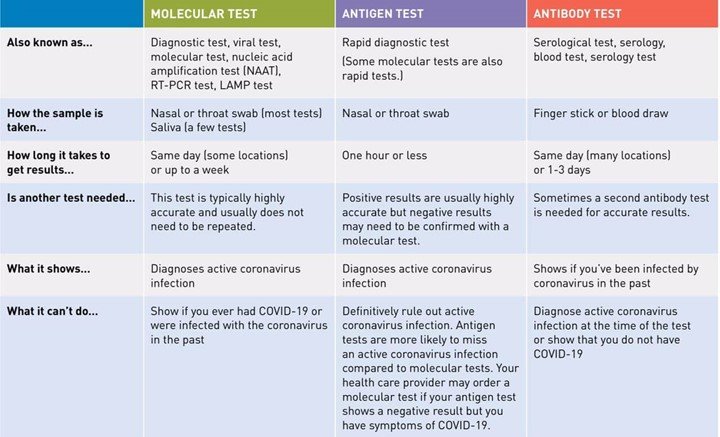
- Currently, there are two types of diagnostic tests which detect the virus –
- molecular tests, such as RT-PCR tests, that detect the virus’s genetic material, &
- antigen tests that detect specific proteins on the surface of the virus.
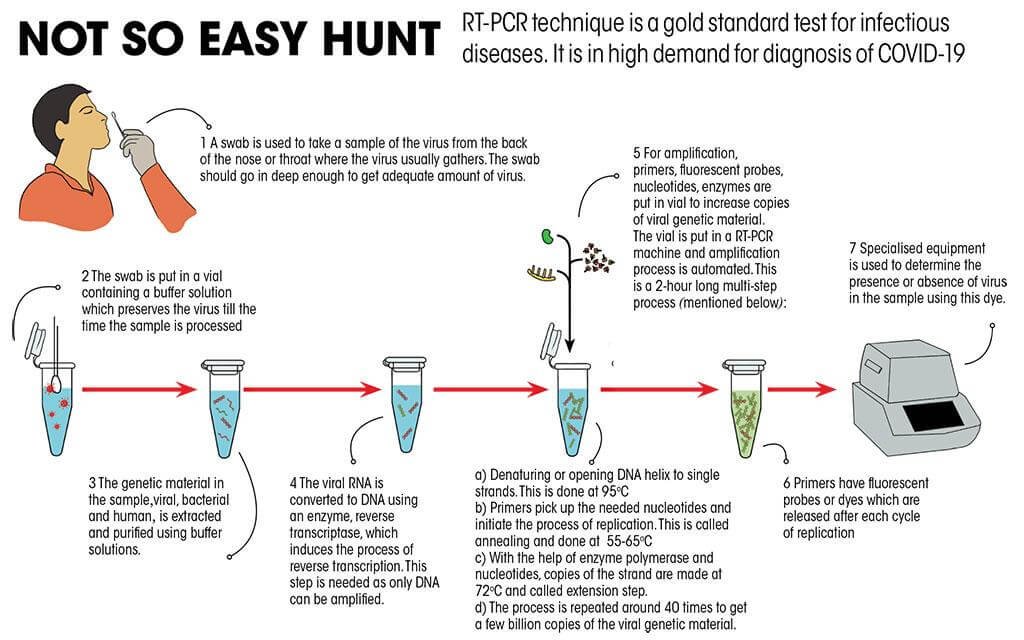
What is the RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction) Test?
- PCR uses the ability of the enzyme, DNA polymerase (enzymes that make the copies of DNA) to synthesize new strands of DNA in a complementary manner to the offered template strand.
- The ‘chain reaction’ is how the DNA fragments are copied, exponentially — one is copied into two, the two are copied into four, & so on.
- But, SARS–COV–2 is a virus made of RNA, which needs to be converted into DNA.
- For this, the technique includes a process called Reverse Transcription (RT).
- A Reverse Transcriptase enzyme converts the RNA into complementary DNA (cDNA).
- RNA is single-stranded & very unstable, which makes it difficult to work with.
- RT-PCR allows the use of RNA as a template. Copies of the DNA are then made & amplified.
- A fluorescent DNA binding dye called the “probe” shows the presence of the virus.
- The test also distinguishes SARS–COV–2 from other viruses.
- Realtime PCRs (RT–PCR) test has brought down the time taken to test samples to 4.5 hours from around 6 hours earlier.
- Currently, diagnosis of active infection is done with the RT-PCR test, the gold standard.
- The RT-PCR test can only tell whether the person has live or very recently dead virus in their body at the time of sample collection.
- RT PCR tests are accurate but require sophisticated equipment & unidirectional settings, trained personnel to run the tests.
- The main difference between PCR & RT-PCR is that PCR uses double-stranded DNA as the template whereas RT-PCR uses RNA as the template.
Link- Source & Credits
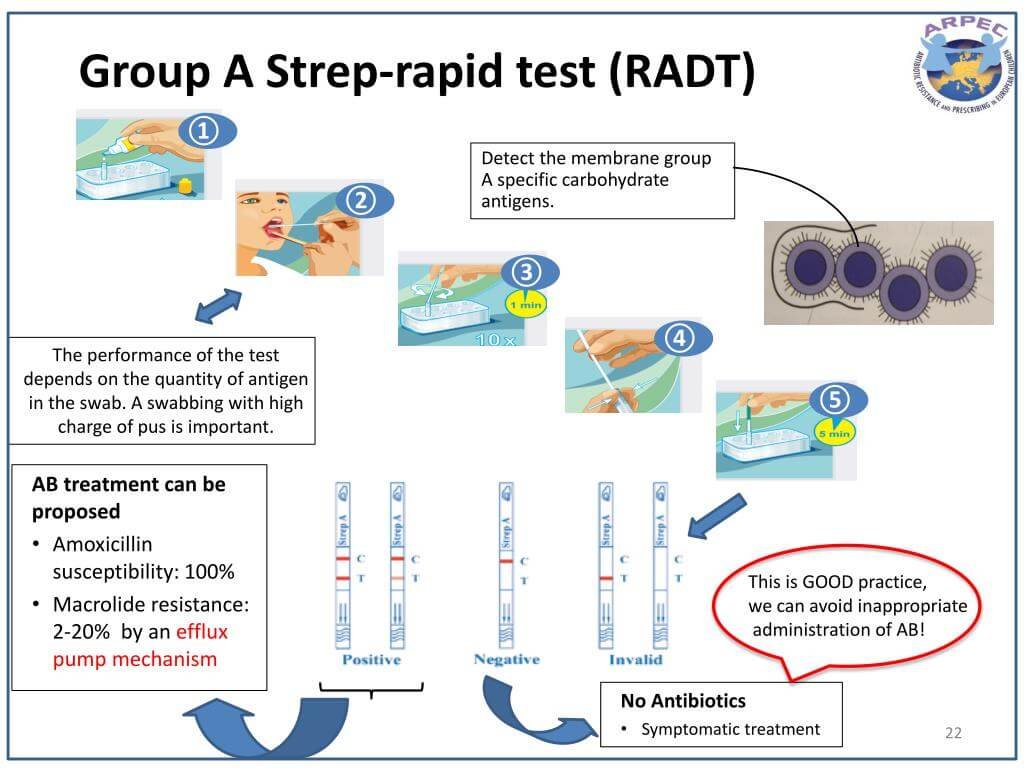
What is the Rapid Antigen Detection Test (RADT), for Covid–19?
- It is a test on swabbed nasal samples that detects antigens (foreign substances that induce an immune response in the body) that are found on or within the SARS–CoV–2 virus.
- It is a point–of–care test, performed outside the conventional laboratory setting, & is used to quickly obtain a diagnostic result.
- Antigen tests usually provide results diagnosing an active coronavirus infection faster than molecular tests, but antigen tests have a higher chance of missing an active infection.
- A swab from the nose is collected for this test, where there’s a high likelihood of virus particles being present.
- Negative results in antigen test need to be confirmed with a PCR test.
- Antigen test can be used as a point of care testing (POC).
- The RT–PCR test takes a minimum of 2–5 hours including the time taken for sample transportation.
- In a reliable rapid antigen detection test, the maximum duration for interpreting a positive or negative test is 30 minutes.
Link- Source & Credits
Antibody Test/Serological Test
- Antibody tests only detect antibodies the immune system develops in response to the virus, not the virus.
- Anti-bodies can show up between 9-28 days after the infection has set in.
- Antibodies are proteins that help fight infections & can provide protection against getting that disease again.
- Antibodies are disease-specific. For example, measles antibodies will protect you from getting measles if you are exposed to it again, but they won’t protect you from getting mumps if you are exposed to mumps.
- Serology tests are crucial for the management & surveillance of the disease.
- These tests offer insight into the virus’s incidence, including symptomatic or asymptomatic infections.
The validity of the antibodies
- Some of the antibodies are short term & some are long term.
- IgM (Immunoglobulin M) antibodies develop early on in an infection whereas IgG (Immunoglobulin G) antibodies against SARS CoV-2 are mostly found after someone has recovered from the infection.
- Antibodies may be detected in our blood for several weeks after we recover from COVID-19.
- Although these antibodies might provide some immunity to the COVID-19 virus, there’s currently not enough evidence to know how long these antibodies last.